As we explained in previous articles, libmodsecurity is a WAF (Web Application Firewall) that allows us to detect certain types of attacks based on predefined rules. Through these signatures, we can detect SQL injections, XSS, LFI, RFI. This time we are going to set up a system in which we will be notified via Telegram when an attack is detected, PF rules will be applied, and a website will be displayed informing about the reason for the ban.
The article is divided into several sections:
- Compiling Nginx
- Installing libmodsecurity
- Whitelisting URLs
- Disabling rules
- Cleaning logs
- Log analysis and banning system
- Installing Redis
- Script modsecurityAnalizer.py
- Script modsecurityNotifier.py
- Script modsecurityPF.py
- PF filtering rules
- Ha-Proxy configuration
- Attackers dashboard
- Useful scripts
- Final result
Compiling Nginx
If we already have Nginx installed, we must check if it was compiled with support for libmodsecurity:
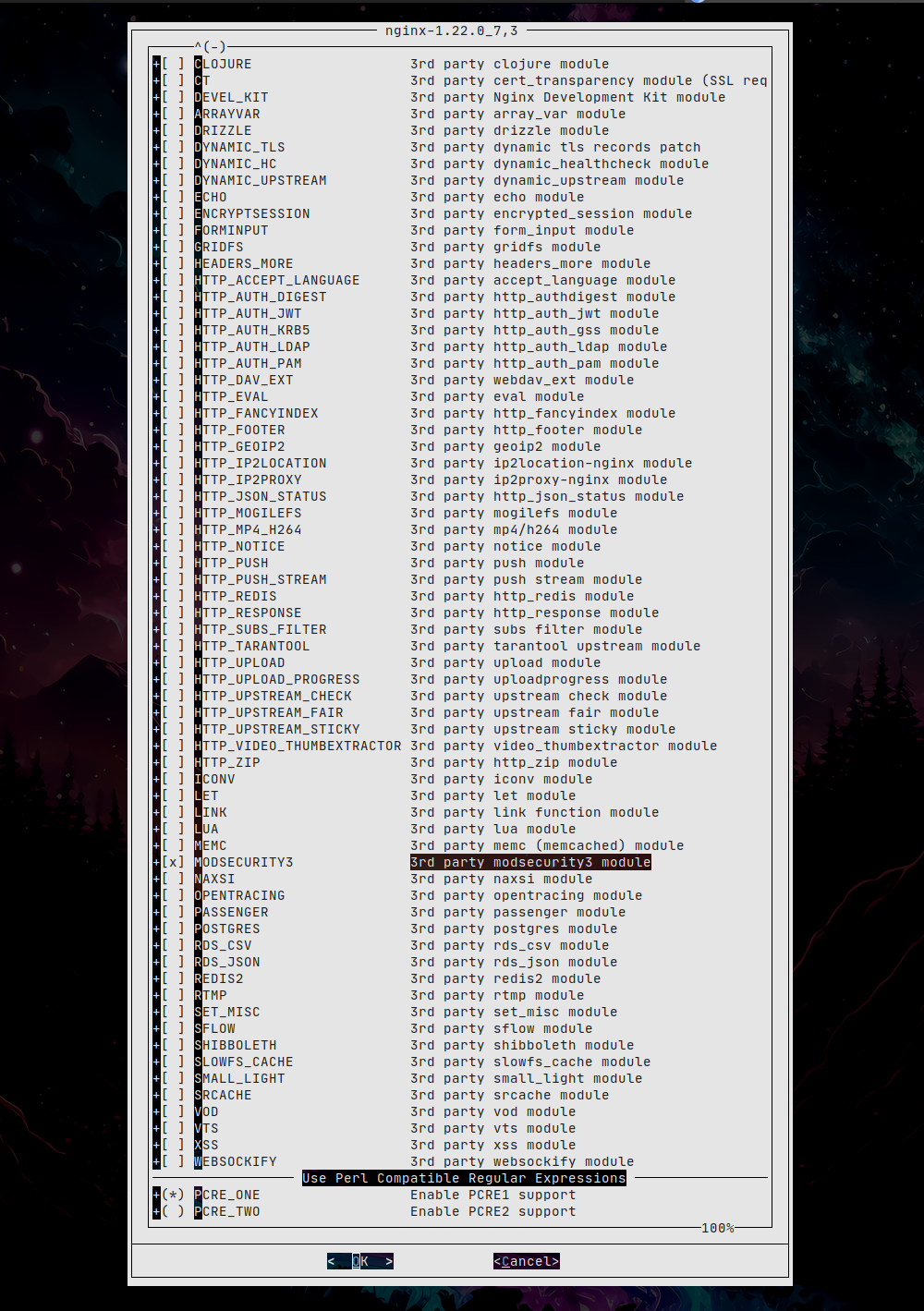
MODSECURITY3 : off
NOTE: The full version (nginx-full) also does not have the option enabled.
In versions prior to June 03, 2020 18:49:04, Nginx had to be compiled with support for modsecurity3, have the modsecurity3 library installed, and also install the modsecurity3-nginx connector. In versions after that date, if we compile Nginx with support for modsecurity3, the connector is already included, but we must add the module loading command in the Nginx configuration. In the old version, this step was unnecessary.
r537834 | joneum | 2020-06-03 20:49:04 +0200 (Wed, 03 Jun 2020) | 11 lines
Merge r532727 from www/nginx-devel:
Convert the following third-party modules to dynamic:
o) accept_language
o) modsecurity3-nginx
Fix the third-party auth_krb5 module build.
Sponsored by: Netzkommune GmbH
If we install modsecurity3-nginx with the new version of Nginx and load the module from the Nginx configuration, we will see the following error:
2020/06/06 14:46:36 [emerg] 24011#101851: module "/usr/local/libexec/nginx/ngx_http_modsecurity_module.so" is not binary compatible in /usr/local/etc/nginx/nginx.conf:4
In addition, pkg will warn us that the modsecurity3-nginx package and nginx conflict with each other since both try to install the same connector.
We compile using ports with the options we want, making sure to enable modsecurity3. Remember that once we switch to ports, we have to manage all packages from ports. You can find more information in this article earlier.
Before compiling and installing Nginx from ports, we uninstall the current version.
We prepare the ports system:
cd /usr/ports
make fetchindex
We perform a search:
Port: nginx-1.22.1_5,3
Path: /usr/ports/www/nginx
Info: Robust and small WWW server
Maint: joneum@FreeBSD.org
B-deps: pcre-8.45_3
R-deps: pcre-8.45_3
WWW: https://nginx.com/
We configure the options:
make config
We compile and install:
make install
We clean temporary files:
Installing libmodsecurity
We install the libmodsecurity library:
make config
make
make install
make clean
We download the OWASP rules:
git clone https://github.com/SpiderLabs/owasp-modsecurity-crs.git
cd owasp-modsecurity-crs
cp crs-setup.conf.example crs-setup.conf
We download the base configuration file for libmodsecurity:
cd /usr/local/etc/modsec
fetch https://raw.githubusercontent.com/SpiderLabs/ModSecurity/v3/master/modsecurity.conf-recommended
fetch https://raw.githubusercontent.com/SpiderLabs/ModSecurity/49495f1925a14f74f93cb0ef01172e5abc3e4c55/unicode.mapping
mv modsecurity.conf-recommended modsecurity.conf
We make sure to have certain parameters with the indicated values:
SecRuleEngine On
SecAuditLogFormat json
SecAuditEngine RelevantOnly
SecAuditLog /var/log/modsec_audit.log
We include the base file and OWASP rules in the main configuration:
# Include the recommended configuration
Include /usr/local/etc/modsec/modsecurity.conf
# OWASP CRS v3 rules
Include /usr/local/owasp-modsecurity-crs/crs-setup.conf
Include /usr/local/owasp-modsecurity-crs/rules/*.conf
We enable libmodsecurity in the Nginx configuration by adding the module load as the first line:
load_module /usr/local/libexec/nginx/ngx_http_modsecurity_module.so;
server {
...
modsecurity on;
modsecurity_rules_file /usr/local/etc/modsec/main.conf;
We restart the service:
We test any type of attack, in my case a MySQL injection with the following payload:
' or '1==1'; --
We will see a new entry in the log and the web request will have been blocked with a 403 Forbidden:
If we are going to generate many entries in the log, it is preferable to write them in concurrent format, so that they will not be logged in a serialized text file, but rather in different files in parallel:
#SecAuditLogType Serial
SecAuditLogType Concurrent
#SecAuditLog /var/log/modsec_audit.log
SecAuditLogStorageDir /opt/modsecurity/var/audit
We restart the service:
We create the directory where to store the log entries:
chown -R www:www /opt/modsecurity/var/audit/
chmod 775 /opt/modsecurity/var/audit/
We install the jq tool, which will be useful for us to view the log information more comfortably:
make config
make
make install
make clean
We check the message field of one of the entries:
"SQL Injection Attack Detected via libinjection"
"Inbound Anomaly Score Exceeded (Total Score: 5)"
NOTE: It is not necessary to filter if we want to see the complete information, we simply pipe the output of cat to a jq without parameters.
Whitelisting URLs
If there is any functionality in our web application that requires a slightly unusual behavior, we can whitelist it so that the rules do not trigger when that section is being processed:
vi /usr/local/owasp-modsecurity-crs/rules/REQUEST-900-EXCLUSION-RULES-BEFORE-CRS.conf
SecRule REQUEST_URI "@beginsWith /CUSTOM_WEB_PATH" \
"id:1001,\
phase:1,\
pass,\
nolog,\
ctl:ruleEngine=Off"
Disabling rules
If, on the other hand, we want to disable a specific rule, we can use the SecRuleRemoveById directive.
NOTE: This directive must be specified after the rule being disabled.
In my case, I was having problems with the rule:
CGI source code leakage
"ruleId": "950140",
"file": "/usr/local/owasp-modsecurity-crs/rules/RESPONSE-950-DATA-LEAKAGES.conf",
"lineNumber": "66",
When displaying code on the web, the alarm goes off because it thinks that the source code of the page itself is being filtered. We add the file of disabled rules:
# Include the recommended configuration
Include /usr/local/etc/modsec/modsecurity.conf
# OWASP CRS v3 rules
Include /usr/local/owasp-modsecurity-crs/crs-setup.conf
Include /usr/local/owasp-modsecurity-crs/rules/*.conf
# Disabled rules
Include /usr/local/etc/modsec/disabledRules.conf
We indicate which rule to disable:
SecRuleRemoveById 950140
However, if we want to disable it only for an IP (necessary if we enable the check in a Ha-Proxy):
SecRule REMOTE_ADDR "@ipMatch IP_ADDRESS" "id:1,phase:1,t:none,nolog,pass,ctl:ruleRemoveById=920280"
Cleaning logs
A good idea is to delete the libmodsecurity logs every X time, for which I have the following CRON enabled:
00 11 * * * /bin/rm -rf /usr/local/bastille/jails/MetaCortex/root/opt/modsecurity/var/audit/* >/dev/null 2>&1
Log analysis and banning system
The system consists of a Redis server and several Python scripts:
- Script for analyzing libmodsecurity logs: modsecurityAnalizer.py
- Script for notification via Telegram, banning through PF and configuration of ACLs and lists in Ha-Proxy: modsecurityNotifier.py
- Script for banning through PF: modsecurityPF.py
Depending on our topology, the scripts will be executed on one server or another. In my case, all services are mounted on the same physical server, so I will execute the modsecurityAnalizer.py and modsecurityNotifier.py scripts on this one, since by blocking through PF I will be filtering for all servers simultaneously.
In case of having a more distributed infrastructure, we must execute modsecurityAnalizer.py on the Nginx where the attacks are received, modsecurityNotifier.py on the Ha-Proxy and modsecurityPF.py on the rest of the servers we want to protect.
| All services on the same parent host | Separated services |
|---|---|
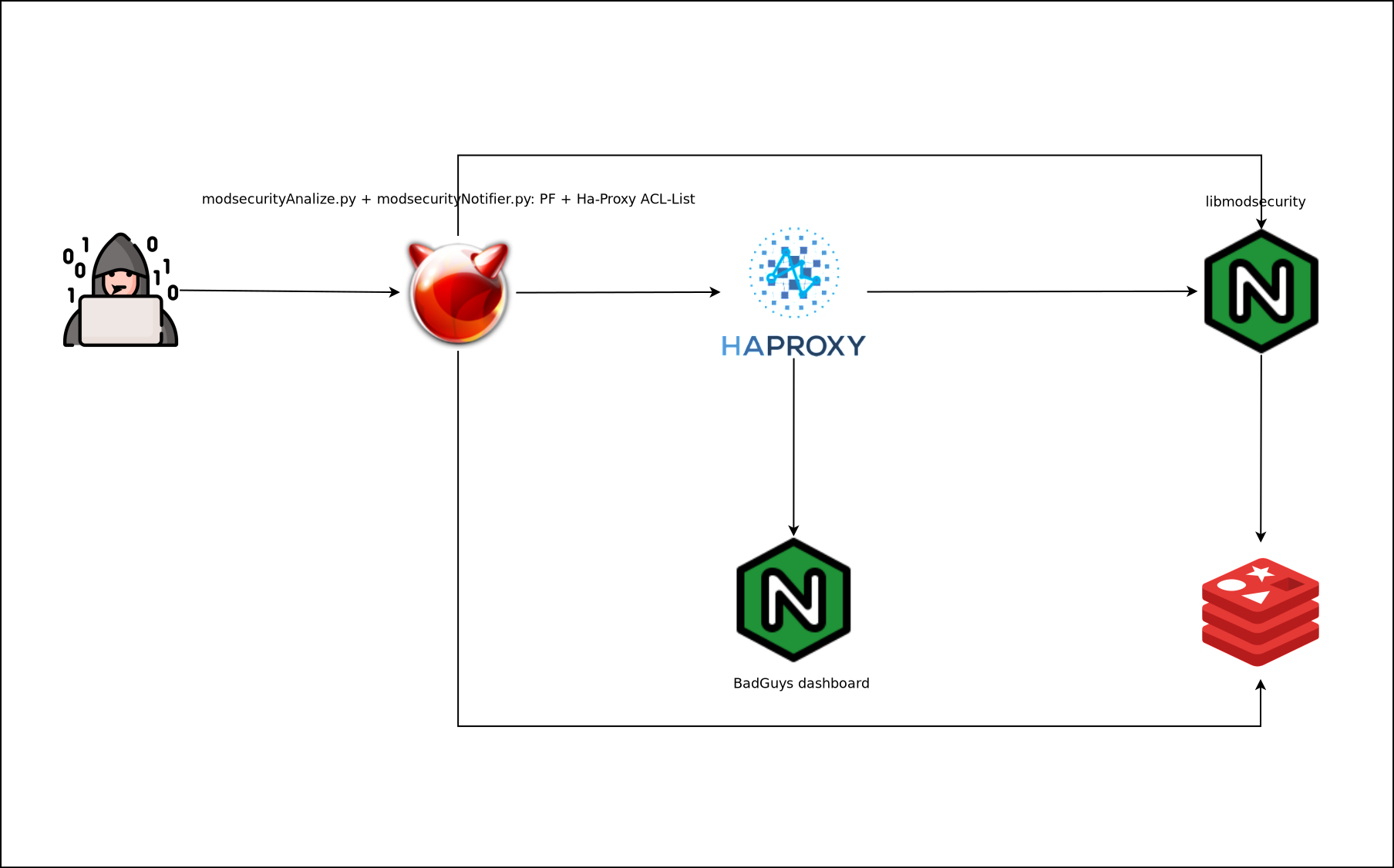
|
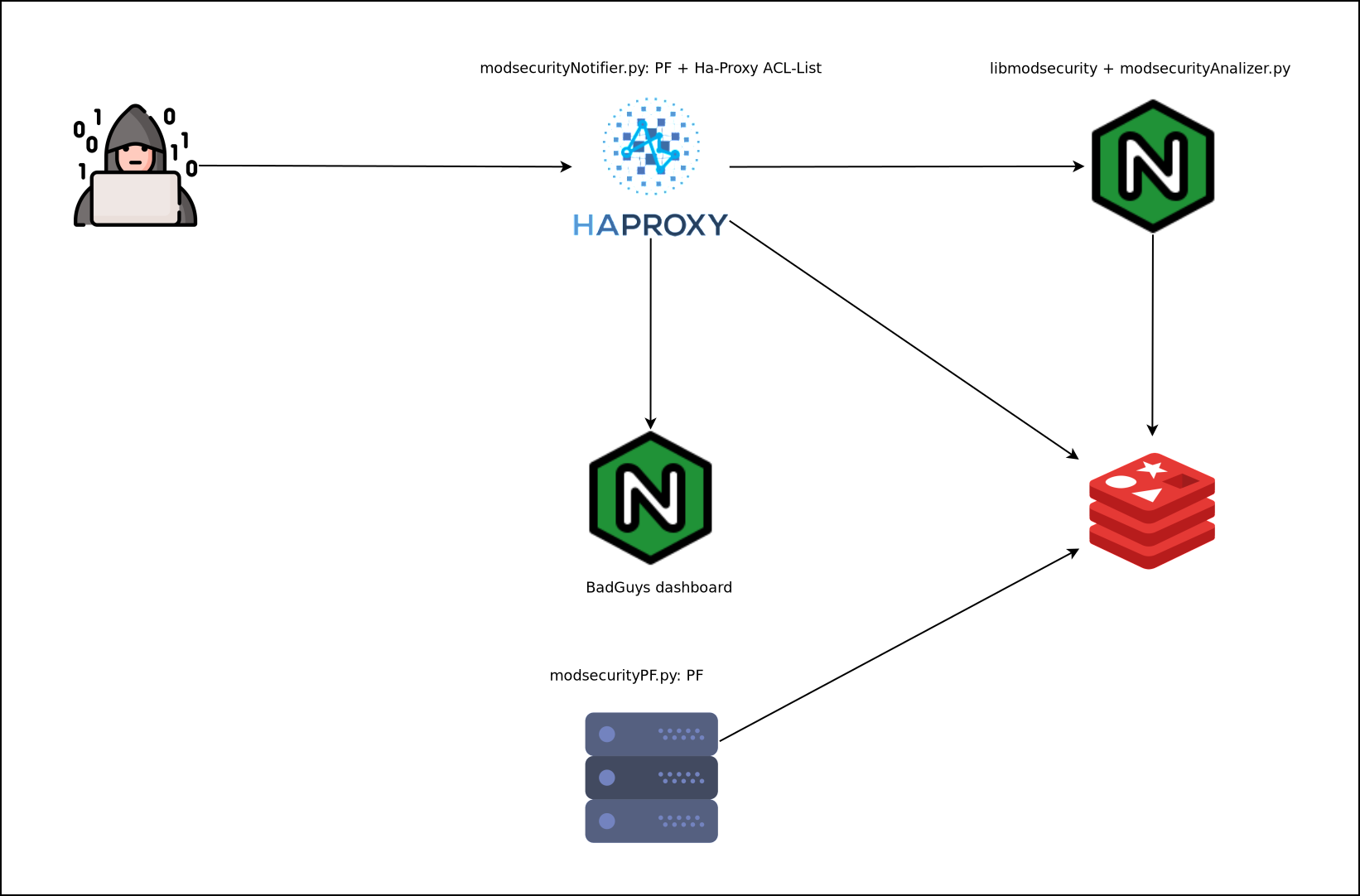
|
The steps for attack banning are:
- Generate logs using libmodsecurity on the Nginx server.
- Read this information from the parent server or the Nginx server and insert it into Redis.
- Read the Redis data from the parent server or Ha-Proxy and configure the rules of PF , also keeping an ACL and a Ha-Proxy list file synchronized.
- Ha-Proxy sends attackers that match the “badguys” ACL to a special backend.
- Attackers are served with a web app that shows information about the attacker, the reason, and the remaining ban time.
- If the infrastructure is distributed, we will execute the modsecurityPF.py script on the rest of the servers, which will simply read from Redis and apply PF rules.
Installing redis
To allow the different scripts to communicate, we will install a Redis server:
We bind it to its IP and assign a password:
bind 192.168.69.2
requirepass XXXXXXXXXX
We enable and start the service:
service redis start
We check the Redis status:
# Server
redis_version:7.0.8
redis_git_sha1:00000000
redis_git_dirty:0
redis_build_id:8e3f49544e856f48
redis_mode:standalone
os:FreeBSD 13.1-RELEASE-p5 amd64
.......
Script modsecurityAnalizer.py
With this script, we will analyze the logs generated by libmodsecurity and generate the associated keys in Redis.
#!/usr/local/bin/python
import sys
import time
from datetime import timedelta
import os
import json
import requests
import redis
from watchdog.observers import Observer
from watchdog.events import FileSystemEventHandler
apikey = "XXXXXXXXXX"
telegramurl = "https://api.telegram.org/bot{}/sendMessage".format(apikey)
userid = "XXXXXXXXXX"
haproxy_ip = '192.168.69.19'
try:
redisconnection = redis.Redis(host="192.168.69.2", port=6379, db=0, password='XXXXXXXXXX')
redisconnection.ping()
except:
print('++ ERROR: Cant connect to redis server')
msg = 'ERROR ' + os.uname().nodename + '(modsecurityAnalizer.py): Cant connect to redis server'
data = {"chat_id":userid, "text":msg}
try:
r = requests.post(telegramurl,json=data)
except:
print("++ Error sending telegram message")
quit()
print("-- Ready to process log files")
class EventHandler(FileSystemEventHandler):
def on_any_event(self, event):
#print("Event type: %s" % event.event_type)
#print("Event file: %s" % event.src_path)
if event.event_type == 'created':
if os.path.isfile(event.src_path):
print('')
print('------------------------------------------------')
print("Processing: %s" % event.src_path)
with open(event.src_path) as fp:
for line in fp:
#print('INSIDE LOOP1: Log lines')
try:
rawdata = json.loads(line)
except:
print('Exception happened loading json data')
continue
for messageline in rawdata['transaction']['messages']:
#print('INSIDE LOOP2: messages')
message = messageline['message']
# Each alert generates two messages one of the real alert another with 'Out/In bound Anomaly Score Exceeded (Total Score: 5)'
if message == 'Outbound Anomaly Score Exceeded (Total Score: 5)' or message == 'Inbound Anomaly Score Exceeded (Total Score: 5)':
continue
print('=====================================')
#print('Message: %s' % message)
data = messageline['details']['data']
#print('data: %s' % data)
# Delete not matched rules messages and anomaly score checks
if message != "":
try:
timestamp = rawdata['transaction']['time_stamp']
except:
timestamp = 'NULL'
try:
attacker = rawdata['transaction']['request']['headers']['x-forwarded-for']
except:
attacker = rawdata['transaction']['client_ip']
if attacker == haproxy_ip:
continue
#attacker = 'NULL'
try:
useragent_platform = rawdata['transaction']['request']['headers']['sec-ch-ua-platform']
except:
useragent_platform = 'NULL'
try:
useragent = rawdata['transaction']['request']['headers']['user-agent']
except:
useragent = 'NULL'
try:
host = rawdata['transaction']['request']['headers']['host']
except:
host = 'NULL'
try:
url = rawdata['transaction']['request']['uri']
except:
url = 'NULL'
try:
method = rawdata['transaction']['request']['method']
except:
method = 'NULL'
try:
payload = messageline['details']['data']
except:
payload = 'NULL'
print('')
print(">> Timestamp: %s" % timestamp)
print("Attacker: %s" % attacker)
print("UserAgentPlatform: %s" % useragent_platform)
print("UserAgent: %s" % useragent)
print("Message: %s" % message)
print("Host: %s" % host)
print("URL: %s" % url)
print("Method: %s" % method)
#print("Payload: %s" % payload)
print(">> Checking redis IP: %s" % attacker)
print("Incrementing redis key value for IP: %s" % attacker)
if redisconnection.get(attacker):
redisconnection.incr(attacker)
else:
redisconnection.incr(attacker)
redisconnection.expire(attacker, timedelta(seconds=3600))
rediscounter = redisconnection.get(attacker)
print("rediscounter: %s" % rediscounter)
print(">> Filling attacker data")
datastring = timestamp + '++' + attacker + '++' + useragent_platform + '++' + useragent + '++' + message + '++' + host + '++' + url + '++' + method + '++' + payload
redisconnection.set('data' + attacker, datastring)
redisconnection.expire('data' + attacker, timedelta(seconds=3600))
db_datastring = redisconnection.get('data' + attacker)
#print("- datastring: %s" % datastring)
#print("- db_datastring: %s" % db_datastring)
print(">> Done")
if __name__ == "__main__":
path = '/usr/local/bastille/jails/MetaCortex/root/opt/modsecurity/var/audit/'
event_handler = EventHandler()
observer = Observer()
observer.schedule(event_handler, path, recursive=True)
observer.start()
try:
while True:
time.sleep(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
observer.stop()
observer.join()
We give it execution permissions:
The service management RC script would be as follows:
#!/bin/sh
#
# PROVIDE: modsecurityAnalizer
# REQUIRE: DAEMON
# KEYWORD: shutdown
. /etc/rc.subr
name=modsecurityAnalizer
rcvar=modsecurityAnalizer_enable
command="/root/.scripts/modsecurityAnalizer.py"
start_cmd="modsecurityAnalizer_start"
stop_cmd="${name}_stop"
status_cmd="${name}_status"
pidfile="/var/run/${name}.pid"
modsecurityAnalizer_start(){
echo "Starting service: ${name}."
/usr/sbin/daemon -c -f -p ${pidfile} ${command}
}
modsecurityAnalizer_stop(){
if [ -f ${pidfile} ]; then
echo "Stopping service: ${name}"
kill -s TERM $(cat ${pidfile})
sleep 3
else
echo "It appears ${name} is not running."
fi
}
modsecurityAnalizer_status(){
if [ -f ${pidfile} ]; then
echo "${name} running with PID: $(cat ${pidfile})"
else
echo "It appears ${name} is not running."
fi
}
load_rc_config $name
run_rc_command "$1"
We assign permissions:
chown root:wheel /usr/local/etc/rc.d/modsecurityAnalizer
We enable the service and start it:
service modsecurityAnalizer start
Script modsecurityNotifier.py
This script will query Redis, notify via Telegram of the received attacks, configure PF rules, and maintain an ACL and a Ha-Proxy list with the attackers’ IPs.
The reason why we will configure ACLs and lists simultaneously is that the ACLs will be inserted by Ha-Proxy’s SocketAdmin, and when Ha-Proxy is restarted, the ACLs disappear. To avoid this, we will also maintain the /usr/local/etc/bagguys.list list so that in case of a restart, the list will contain the same IPs as those in the ACL.
#!/usr/local/bin/python
import redis
import requests
import subprocess
import time
import os
import re
from haproxyadmin import haproxy
apikey = "XXXXXXXXXX"
telegramurl = "https://api.telegram.org/bot{}/sendMessage".format(apikey)
userid = "XXXXXXXXXX"
HaProxyBlacklistFile = "/usr/local/bastille/jails/Atlas/root/usr/local/etc/bagguys.list"
HaProxyAdminSocketDir = "/usr/local/bastille/jails/Atlas/root/var/run/"
BadguysAclPattern = ".*\(/usr/local/etc/bagguys\.list\) pattern loaded from file '/usr/local/etc/bagguys\.list'.*"
try:
redisconnection = redis.Redis(host="192.168.69.2", port=6379, db=0, password='XXXXXXXXXX', charset="utf-8", decode_responses=True)
redisconnection.ping()
except:
print('++ ERROR: Cant connect to redis server')
msg = 'ERROR ' + os.uname().nodename + '(modsecurityNotifier.py): Cant connect to redis server'
data = {"chat_id":userid, "text":msg}
try:
r = requests.post(telegramurl,json=data)
except:
print("++ Error sending telegram message")
quit()
while(True):
print('')
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('>> Checking REDIS content')
print('------------------------------------------------')
for attacker in redisconnection.scan_iter():
#print("-- Analyzing key: %s" % attacker)
if attacker[0:4] == 'data' or attacker[0:9] == 'geoipdata':
continue
else:
rediscounter = redisconnection.get(attacker)
print("Attacker: %s Counter: %s" % (attacker, rediscounter))
if int(rediscounter) >= 5 and redisconnection.get('data' + attacker):
data = redisconnection.get('data' + attacker)
#print("Data: %s" % data)
timestamp = data.split('++')[0]
print("timestamp: %s" % timestamp)
attacker = data.split('++')[1]
print("attacker: %s" % attacker)
useragent_platform = data.split('++')[2]
print("useragent_platform: %s" % useragent_platform)
useragent = data.split('++')[3]
print("useragent: %s" % useragent)
message = data.split('++')[4]
print("message: %s" % message)
host = data.split('++')[5]
print("host: %s" % host)
url = data.split('++')[6]
print("url: %s" % url)
method = data.split('++')[7]
print("method: %s" % method)
payload = data.split('++')[8]
#print("payload: %s" % payload)
print('------------------------------------------------')
print(">> Trying to ban attacker ip readed from Redis: %s" % attacker)
print('------------------------------------------------')
bannedhosts = subprocess.run(["pfctl", "-t", "badguys", "-T", "show"], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, text=True)
print("PF Banned hosts: \n%s" % bannedhosts.stdout)
blockattacker = 1
for bannedhost in bannedhosts.stdout.split(' '):
bannedhost = bannedhost.replace("\n", "")
if bannedhost == '':
continue
print("Comparing Redis:%s --> PF:%s" % (attacker, bannedhost))
if attacker == bannedhost:
print("Attacker already banned, aborting")
blockattacker = 0
break
#print("blockattacker var value: %s" % blockattacker)
if blockattacker == 1:
print("-- Banning time for: %s" % attacker)
cmd = '/sbin/pfctl -t badguys -T add ' + attacker
cmdreturnvalue = subprocess.call(cmd, shell=True)
print("cmdreturnvalue: %s" % cmdreturnvalue)
if cmdreturnvalue != 0:
print("++ ERROR: Cant add attacker ip to PF badguys table")
print("-- Killing established connections: %s" % attacker)
cmd = '/sbin/pfctl -k ' + attacker
cmdreturnvalue = subprocess.call(cmd, shell=True)
print("cmdreturnvalue: %s" % cmdreturnvalue)
if cmdreturnvalue != 0:
print("++ ERROR: Cant kill established connections")
print('-- Adding to HA-Proxy badguys blacklist file')
HaProxyBlacklist = open(HaProxyBlacklistFile, "a")
HaProxyBlacklist.write(attacker+"\n")
HaProxyBlacklist.close()
print('-- Adding to HA-Proxy ACL via AdminSocket')
try:
hap = haproxy.HAProxy(socket_dir=HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = True
except:
print('ERRRO: Cant connect to AdminSocket: %S so its impossible to add attacker IP to blacklist ACL' % HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = False
if canConnectToAdminSocket:
aclCounter = 0
badguysAclFound = 0
for acl in hap.show_acl():
if acl[0] == '#':
continue
#print("ACL: %s" % acl)
#print("Content: %s" % hap.show_acl(aclCounter))
#print("Comparing ACL: %s -> RegExp: %s" % (acl,BadguysAclPattern))
if re.match(BadguysAclPattern, acl):
print("> MATCH - BadGuys Acl: %s" % aclCounter)
badguysAclFound = 1
break
aclCounter = aclCounter + 1
if badguysAclFound == 1:
print('Current Content: %s' % hap.show_acl(aclCounter))
hap.add_acl(aclCounter, attacker)
print('Post ADD Content: %s' % hap.show_acl(aclCounter))
else:
print('>> ERROR: Cant locate ACL so its impossible to add attacker IP to blacklist')
msg = "-- Banning time for: " + attacker
data = {"chat_id":userid, "text":msg}
try:
r = requests.post(telegramurl,json=data)
except:
print("++ Error sending telegram message")
continue
print("-- Sending telegram alert")
msg = 'Date: ' + str(timestamp) + '\nAttacker: ' + str(attacker) + '\nUserAgentPlatform: ' + str(useragent_platform) + '\nUserAgent: ' + str(useragent) + '\nHost: ' + str(host) + '\nUrl: ' + str(url) + '\nAlert: ' + str(message) + '\nPayload: ' + str(payload)
data = {"chat_id":userid, "text":msg}
try:
r = requests.post(telegramurl,json=data)
except:
print("++ Error sending telegram message")
continue
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('')
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('>> Clearing old PF ips')
print('------------------------------------------------')
bannedhosts = subprocess.run(["pfctl", "-t", "badguys", "-T", "show"], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, text=True)
for bannedhost in bannedhosts.stdout.split(' '):
bannedhost = bannedhost.replace("\n", "")
if bannedhost == '':
continue
redis_found = False
for attacker in redisconnection.scan_iter():
if attacker[0:4] == 'data' or attacker[0:9] == 'geoipdata':
continue
else:
print("Comparing PF:%s --> Redis:%s" % (bannedhost, attacker))
if bannedhost == attacker:
redis_found = True
break
if redis_found == False:
print('-- Unbaning: %s' % bannedhost)
cmd = '/sbin/pfctl -t badguys -T delete ' + bannedhost
cmdreturnvalue = subprocess.call(cmd, shell=True)
print("cmdreturnvalue: %s" % cmdreturnvalue)
if cmdreturnvalue != 0:
print("++ ERROR: Cant unban attacker ip from PF badguys table")
else:
print('Attacker already present in Redis, preserving banning: %s' % bannedhost)
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('')
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('>> Clearing old blacklisted HA-Proxy file')
print('------------------------------------------------')
if os.path.exists(HaProxyBlacklistFile):
bannedhosts = []
HaProxyBlacklist = open(HaProxyBlacklistFile, 'r')
for bannedhost in HaProxyBlacklist.readlines():
bannedhost = bannedhost.replace("\n", "")
#print(bannedhost)
redis_found = False
for attacker in redisconnection.scan_iter():
if attacker[0:4] == 'data' or attacker[0:9] == 'geoipdata':
continue
else:
print("Comparing HA:%s --> Redis:%s" % (bannedhost, attacker))
if bannedhost == attacker:
redis_found = True
break
if redis_found == False:
print('-- Unblacklisting: %s' % bannedhost)
else:
print('Attacker already present in Redis, preserving blacklisting: %s' % bannedhost)
bannedhosts.append(bannedhost)
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('bannedhosts: %s' % bannedhosts)
with open(HaProxyBlacklistFile, 'w') as HaProxyBlacklist:
for bannedhost in bannedhosts:
HaProxyBlacklist.write(bannedhost+'\n')
print('')
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('>> Clearing old blacklisted HA-Proxy ACL')
print('------------------------------------------------')
try:
hap = haproxy.HAProxy(socket_dir=HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = True
except:
print('ERRRO: Cant connect to AdminSocket: %s so its impossible to delete attacker IP from blacklist ACL' % HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = False
if canConnectToAdminSocket:
aclCounter = 0
badguysAclFound = 0
for acl in hap.show_acl():
if acl[0] == '#':
continue
if re.match(BadguysAclPattern, acl):
print("> MATCH - BadGuys Acl: %s" % aclCounter)
badguysAclFound = 1
break
aclCounter = aclCounter + 1
if badguysAclFound == 1:
print('Current Content: %s' % hap.show_acl(aclCounter))
for aclAttackerRaw in hap.show_acl(aclCounter):
aclAttacker = aclAttackerRaw.split(' ')[1]
redis_found = False
for attacker in redisconnection.scan_iter():
if attacker[0:4] == 'data' or attacker[0:9] == 'geoipdata':
continue
else:
print("Comparing ACL:%s --> Redis:%s" % (aclAttacker, attacker))
if aclAttacker == attacker:
redis_found = True
break
if redis_found == False:
print('-- Unblacklisting: %s' % aclAttacker)
hap.del_acl(aclCounter, aclAttackerRaw)
print('Post DEL Content: %s' % hap.show_acl(aclCounter))
else:
print('Attacker already present in Redis, preserving blacklisting: %s' % aclAttacker)
print('------------------------------------------------')
else:
print('>> ERROR: Cant locate ACL so its impossible to del attacker IP from blacklist')
time.sleep(5)
We give it execution permissions:
The service management RC script would be as follows:
#!/bin/sh
#
# PROVIDE: modsecurityNotifier
# REQUIRE: DAEMON
# KEYWORD: shutdown
. /etc/rc.subr
name=modsecurityNotifier
rcvar=modsecurityNotifier_enable
command="/root/.scripts/modsecurityNotifier.py"
start_cmd="modsecurityNotifier_start"
stop_cmd="modsecurityNotifier_stop"
status_cmd="modsecurityNotifier_status"
pidfile="/var/run/${name}.pid"
modsecurityNotifier_start(){
echo "Starting service: ${name}."
/usr/sbin/daemon -c -f -p ${pidfile} ${command}
}
modsecurityNotifier_stop(){
if [ -f ${pidfile} ]; then
echo "Stopping service: ${name}"
kill -s INT $(cat ${pidfile})
sleep 3
else
echo "It appears ${name} is not running."
fi
}
modsecurityNotifier_status(){
if [ -f ${pidfile} ]; then
echo "${name} running with PID: $(cat ${pidfile})"
else
echo "It appears ${name} is not running."
fi
}
load_rc_config $name
run_rc_command "$1"
We assign permissions:
chown root:wheel /usr/local/etc/rc.d/modsecurityNotifier
We enable and start the service:
service modsecurityNotifier start
Script modsecurityPF.py
We will only use the following script if we have a distributed infrastructure. We will run it on the rest of the servers that do not depend on Ha-Proxy, such as web servers, databases, etc.
#!/usr/local/bin/python
import redis
import subprocess
import time
import os
apikey = "XXXXXXXXXX"
telegramurl = "https://api.telegram.org/bot{}/sendMessage".format(apikey)
userid = "XXXXXXXXXX"
try:
redisconnection = redis.Redis(host="192.168.69.2", port=6379, db=0, password='XXXXXXXXXX', charset="utf-8", decode_responses=True)
redisconnection.ping()
except:
print('++ ERROR: Cant connect to redis server')
msg = 'ERROR ' + os.uname().nodename + '(modsecurityPF.py): Cant connect to redis server'
data = {"chat_id":userid, "text":msg}
try:
r = requests.post(telegramurl,json=data)
except:
print("++ Error sending telegram message")
quit()
while(True):
print('')
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('>> Checking REDIS content')
print('------------------------------------------------')
for attacker in redisconnection.scan_iter():
#print("-- Analyzing key: %s" % attacker)
if attacker[0:4] == 'data' or attacker[0:9] == 'geoipdata':
continue
else:
rediscounter = redisconnection.get(attacker)
print("Attacker: %s Counter: %s" % (attacker, rediscounter))
if int(rediscounter) >= 5 and redisconnection.get('data' + attacker):
data = redisconnection.get('data' + attacker)
#print("Data: %s" % data)
timestamp = data.split('++')[0]
print("timestamp: %s" % timestamp)
attacker = data.split('++')[1]
print("attacker: %s" % attacker)
useragent = data.split('++')[2]
print("useragent: %s" % useragent)
message = data.split('++')[3]
print("message: %s" % message)
host = data.split('++')[4]
print("host: %s" % host)
url = data.split('++')[5]
print("url: %s" % url)
method = data.split('++')[6]
print("method: %s" % method)
payload = data.split('++')[7]
#print("payload: %s" % payload)
print('------------------------------------------------')
print(">> Trying to ban attacker ip readed from Redis: %s" % attacker)
print('------------------------------------------------')
bannedhosts = subprocess.run(["pfctl", "-t", "badguys", "-T", "show"], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, text=True)
print("PF Banned hosts: \n%s" % bannedhosts.stdout)
blockattacker = 1
for bannedhost in bannedhosts.stdout.split(' '):
bannedhost = bannedhost.replace("\n", "")
if bannedhost == '':
continue
print("Comparing Redis:%s --> PF:%s" % (attacker, bannedhost))
if attacker == bannedhost:
print("Attacker already banned, aborting")
blockattacker = 0
break
#print("blockattacker var value: %s" % blockattacker)
if blockattacker == 1:
print("-- Banning time for: %s" % attacker)
cmd = '/sbin/pfctl -t badguys -T add ' + attacker
cmdreturnvalue = subprocess.call(cmd, shell=True)
print("cmdreturnvalue: %s" % cmdreturnvalue)
if cmdreturnvalue != 0:
print("++ ERROR: Cant add attacker ip to PF badguys table")
print("-- Killing established connections: %s" % attacker)
cmd = '/sbin/pfctl -k ' + attacker
cmdreturnvalue = subprocess.call(cmd, shell=True)
print("cmdreturnvalue: %s" % cmdreturnvalue)
if cmdreturnvalue != 0:
print("++ ERROR: Cant kill established connections")
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('')
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('>> Clearing old PF ips')
print('------------------------------------------------')
bannedhosts = subprocess.run(["pfctl", "-t", "badguys", "-T", "show"], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, text=True)
for bannedhost in bannedhosts.stdout.split(' '):
bannedhost = bannedhost.replace("\n", "")
if bannedhost == '':
continue
redis_found = False
for attacker in redisconnection.scan_iter():
if attacker[0:4] == 'data' or attacker[0:9] == 'geoipdata':
continue
else:
print("Comparing PF:%s --> Redis:%s" % (bannedhost, attacker))
if bannedhost == attacker:
redis_found = True
break
if redis_found == False:
print('-- Unbaning: %s' % bannedhost)
cmd = '/sbin/pfctl -t badguys -T delete ' + bannedhost
cmdreturnvalue = subprocess.call(cmd, shell=True)
print("cmdreturnvalue: %s" % cmdreturnvalue)
if cmdreturnvalue != 0:
print("++ ERROR: Cant unban attacker ip from PF badguys table")
else:
print('Attacker already present in Redis, preserving banning: %s' % bannedhost)
print('------------------------------------------------')
time.sleep(5)
We give it execution permissions:
The service management RC script would be as follows:
#!/bin/sh
#
# PROVIDE: modsecurityPF
# REQUIRE: DAEMON
# KEYWORD: shutdown
. /etc/rc.subr
name=modsecurityPF
rcvar=modsecurityPF_enable
command="/root/.scripts/modsecurityPF.py"
start_cmd="modsecurityPF_start"
stop_cmd="modsecurityPF_stop"
status_cmd="modsecurityPF_status"
pidfile="/var/run/${name}.pid"
modsecurityPF_start(){
echo "Starting service: ${name}."
/usr/sbin/daemon -c -f -p ${pidfile} ${command}
}
modsecurityPF_stop(){
if [ -f ${pidfile} ]; then
echo "Stopping service: ${name}"
kill -s INT $(cat ${pidfile})
sleep 3
else
echo "It appears ${name} is not running."
fi
}
modsecurityPF_status(){
if [ -f ${pidfile} ]; then
echo "${name} running with PID: $(cat ${pidfile})"
else
echo "It appears ${name} is not running."
fi
}
load_rc_config $name
run_rc_command "$1"
We assign permissions:
chown root:wheel /usr/local/etc/rc.d/modsecurityPF
We enable and start the service:
service modsecurityPF start
PF filtering rules
To block traffic from PF, we will use a table called badguys. All traffic coming from these IPs will be blocked, except for port 80/443 if it is Ha-Proxy. In the rest of the servers, it would be exactly the same but removing the lines:
# Continue attending badguys in HA-Proxy, we have a surprise for them:
pass in quick proto tcp from <badguys> to 192.168.69.19 port 80
pass in quick proto tcp from <badguys> to 192.168.69.19 port 443
ext_if = "nfe0"
set block-policy return
scrub in on $ext_if all fragment reassemble
set skip on lo
table <badguys> persist
table <jails> persist
nat on $ext_if from <jails> to any -> ($ext_if:0)
rdr-anchor "rdr/*"
antispoof for $ext_if inet
block log all
pass out quick
pass in proto tcp to 192.168.69.2 port 7777
# SMTP -> HellStorm
pass in proto tcp to 192.168.69.17 port 25
# HTTP/HTTPS -> Atlas
pass in proto tcp to 192.168.69.19 port 80
pass in proto tcp to 192.168.69.19 port 443
# Continue attending badguys in HA-Proxy, we have a surprise for them:
pass in quick proto tcp from <badguys> to 192.168.69.19 port 80
pass in quick proto tcp from <badguys> to 192.168.69.19 port 443
# Xbox -> Paradox
pass in proto tcp from 192.168.69.196 to 192.168.69.18 port 80
# TARS -> Paradox
pass in proto tcp from 192.168.69.198 to 192.168.69.18 port 80
# Garrus -> Paradox, testing purpose
pass in proto tcp from 192.168.69.4 to 192.168.69.18 port 80
pass in proto tcp to any port 22
# Block all traffic from badguys, except 80,443 that was allowed previously:
block in from <badguys>
Ha-Proxy Configuration
As we have already mentioned, the idea is to keep the HA-Proxy ACLs synchronized in running-config using the AdminSocket and a list of IPs in a file in the file system. This way, if the Ha-Proxy is restarted, everything will continue to work, as it will read the file that also has the list of IPs.
The Ha-Proxy configuration would be as follows:
global
daemon
maxconn 5000
log 192.168.69.19:514 local1
user nobody
group nobody
stats socket /var/run/haproxy.sock user nobody group nobody mode 660 level admin
ssl-default-bind-ciphers ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
ssl-default-bind-options ssl-min-ver TLSv1.2 no-tls-tickets
defaults
timeout connect 10s
timeout client 30s
timeout server 30s
mode http
# ENABLE LOGGING:
# TCP connections
#log global
# Backend connections
#option httplog
listen stats
bind *:8404
stats enable
stats uri /stats
stats refresh 5s
stats auth kr0m:8XEn3EL1aYIeKI
frontend HTTP
bind :80
# Allow LetsEncrypt certificate renew and redirect to HTTPS all other requests:
acl letsencrypt path_beg /.well-known/acme-challenge/
http-request redirect scheme https unless letsencrypt
use_backend letsencrypt-backend if letsencrypt
frontend HTTP-SSL
bind :443 ssl crt /usr/local/etc/haproxy_certs.pem
http-request add-header X-Forwarded-Proto https
acl mail hdr_dom(host) mail.alfaexploit.com
acl prometheus hdr_dom(host) prometheus.alfaexploit.com
acl grafana hdr_dom(host) grafana.alfaexploit.com
acl gdrive hdr_dom(host) gdrive.alfaexploit.com
acl www_alfaexploit hdr_dom(host) www.alfaexploit.com
acl badguys_alfaexploit hdr_dom(host) badguys.alfaexploit.com
acl alfaexploit hdr_dom(host) alfaexploit.com
http-request deny deny_status 400 if !mail !prometheus !grafana !gdrive !www_alfaexploit !badguys_alfaexploit !alfaexploit
# Show banned list to anyone who wants to view it
use_backend badguys if badguys_alfaexploit
# Route Badguys traffic:
acl badguy_ips src -f /usr/local/etc/bagguys.list
use_backend badguys if badguy_ips
# Order matters because acl alfaexploit -> alfaexploit.com is the most generic that covers all of them
use_backend mail if mail
use_backend prometheus if prometheus
use_backend prometheus if grafana
use_backend gdrive if gdrive
use_backend alfaexploit if www_alfaexploit
use_backend alfaexploit if alfaexploit
backend letsencrypt-backend
server letsencrypt 192.168.69.19:88
backend mail
server HellStorm 192.168.69.17:80 check send-proxy-v2
backend prometheus
server RECLog 192.168.69.21:80 check send-proxy-v2
backend gdrive
server Paradox 192.168.69.18:8080 check send-proxy-v2
backend alfaexploit
server MetaCortex 192.168.69.20:80 check send-proxy-v2
backend badguys
http-request set-path / unless { path_beg /images }
server Atlas 192.168.69.19:8888 check send-proxy-v2
Attackers Dashboard
On the server where we will have the attackers dashboard, we will install Nginx and PHP:
We enable and start the PHP service:
service php-fpm start
We include our configuration from the global Nginx file:
http {
include badguys.conf;
server {
listen 192.168.69.19:8888 proxy_protocol;
server_name badguys.alfaexploit.com;
set_real_ip_from 192.168.69.19;
real_ip_header proxy_protocol;
root /usr/local/www/nginx;
index index.php;
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(.*)$;
fastcgi_keep_conn on;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
}
}
We enable and start the Nginx service:
service nginx start
We create the directory to store the logos of the operating systems:
We download the logos of the operating systems:
wget https://alfaexploit.com/files/libmodSecurityFreeBSD/images.tar.gz
tar xvzf images.tar.gz<>
The dashboard code would be as follows:
<?php
$os_array = [
'windows nt 10' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows nt 6.3' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows nt 6.2' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows nt 6.1|windows nt 7.0' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows nt 6.0' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows nt 5.2' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows nt 5.1' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows xp' => 'WindowsXP',
'windows nt 5.0|windows nt5.1|windows 2000' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows me' => 'WindowsME',
'windows nt 4.0|winnt4.0' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows ce' => 'WindowsCE',
'windows 98|win98' => 'Windows98',
'windows 95|win95' => 'Windows95',
'win16' => 'Windows16',
'mac os x 10.1[^0-9]' => 'MacOS',
'macintosh|mac os x' => 'MacOS',
'mac_powerpc' => 'MacOS',
'ubuntu' => 'Linux',
'iphone' => 'iPhone',
'ipod' => 'iPod',
'ipad' => 'iPad',
'android' => 'Android',
'blackberry' => 'BlackBerry',
'webos' => 'WebOS',
'linux' => 'Linux',
'(media center pc).([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2})'=>'WindowsMediaCenter',
'(win)([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9x]{1,2})'=>'Windows',
'(win)([0-9]{2})'=>'Windows',
'(windows)([0-9x]{2})'=>'Windows',
'Win 9x 4.90'=>'WindowsME',
'(windows)([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2})'=>'Windows',
'win32'=>'Windows',
'(java)([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2})'=>'Java',
'(Solaris)([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9x]{1,2}){0,1}'=>'Solaris',
'dos x86'=>'DOS',
'Mac OS X'=>'MacOS',
'Mac_PowerPC'=>'MacOS',
'(mac|Macintosh)'=>'MacOS',
'(sunos)([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2}){0,1}'=>'SunOS',
'(beos)([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2}){0,1}'=>'BeOS',
'(risc os)([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2})'=>'RISCOS',
'unix'=>'Unix',
'os/2'=>'OS2',
'freebsd'=>'FreeBSD',
'openbsd'=>'OpenBSD',
'netbsd'=>'NetBSD',
'irix'=>'IRIX',
'plan9'=>'Plan9',
'aix'=>'AIX',
'GNU Hurd'=>'GNUHurd',
'(fedora)'=>'Linux',
'(kubuntu)'=>'Linux',
'(ubuntu)'=>'Linux',
'(debian)'=>'Linux',
'(CentOS)'=>'Linux',
'(Mandriva).([0-9]{1,3}(\.[0-9]{1,3})?(\.[0-9]{1,3})?)'=>'Linux',
'(SUSE).([0-9]{1,3}(\.[0-9]{1,3})?(\.[0-9]{1,3})?)'=>'Linux',
'(Dropline)'=>'Linux',
'(ASPLinux)'=>'Linux',
'(Red Hat)'=>'Linux',
'(linux)'=>'Linux',
'(amigaos)([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2})'=>'AmigaOS',
'amiga-aweb'=>'AmigaOS',
'amiga'=>'AmigaOS',
'AvantGo'=>'PalmOS',
'[0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,3}'=>'Linux',
'(webtv)/([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2})'=>'WebTV',
'Dreamcast'=>'DreamcastOS',
'GetRight'=>'Windows',
'go!zilla'=>'Windows',
'gozilla'=>'Windows',
'gulliver'=>'Windows',
'ia archiver'=>'Windows',
'NetPositive'=>'Windows',
'mass downloader'=>'Windows',
'microsoft'=>'Windows',
'offline explorer'=>'Windows',
'teleport'=>'Windows',
'web downloader'=>'Windows',
'webcapture'=>'Windows',
'webcollage'=>'Windows',
'webcopier'=>'Windows',
'webstripper'=>'Windows',
'webzip'=>'Windows',
'wget'=>'Wget',
'Java'=>'Java',
'flashget'=>'FlashGet',
'MS FrontPage'=>'Windows',
'(msproxy)/([0-9]{1,2}.[0-9]{1,2})'=>'Windows',
'(msie)([0-9]{1,2}.[0-9]{1,2})'=>'Windows',
'libwww-perl'=>'Perl',
'UP.Browser'=>'WindowsCE',
'NetAnts'=>'Windows',
];
function user_agent_os($user_agent, $os_array) {
foreach ($os_array as $regex => $value) {
if (preg_match('{\b('.$regex.')\b}i', $user_agent)) {
return $value;
#$key = array_rand($os_array);
#$value = $os_array[$key];
#return $value;
}
}
return 'Unknown';
}
function secs_to_str ($duration) {
$periods = array(
'day' => 86400,
'hour' => 3600,
'minute' => 60,
'second' => 1
);
$parts = array();
foreach ($periods as $name => $dur) {
$div = floor($duration / $dur);
if ($div == 0)
continue;
else
if ($div == 1)
$parts[] = $div . " " . $name;
else
$parts[] = $div . " " . $name . "s";
$duration %= $dur;
}
$last = array_pop($parts);
if (empty($parts))
return $last;
else
return join(', ', $parts) . " and " . $last;
}
if (!empty($_SERVER['HTTP_CLIENT_IP'])) {
$ip_address = $_SERVER['HTTP_CLIENT_IP'];
}
elseif (!empty($_SERVER['HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR'])) {
$ip_address = $_SERVER['HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR'];
}
else {
$ip_address = $_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR'];
}
$redis = new Redis();
$redis->connect('192.168.69.2', 6379);
$redis->auth('XXXXXXXX');
$allKeys = $redis->keys('*');
echo "<!DOCTYPE html>";
echo "<html>";
echo "<head>";
echo "<style>";
echo ".attacker_data {";
echo "position: relative;";
echo "top: -6px;";
echo "padding-left: 8px;";
echo "}";
echo "table, td, th {";
echo "border: 1px solid black;";
echo "margin-bottom: 15px;";
echo "}";
echo "table {";
echo " border-collapse: collapse;";
echo " width: 100%;";
echo "}";
echo "td {";
echo " text-align: center;";
echo "}";
echo "</style>";
echo "</head>";
echo "<body>";
echo "<table>";
echo "<tr>";
echo "<td>Date</td>";
echo "<td>IP</td>";
echo "<td>I'm watching you</td>";
echo "<td>Attack</td>";
echo "<td>Unban remaining time</td>";
echo "</tr>";
foreach ($allKeys as $key) {
$attacker_data = array();
if (str_starts_with($key, 'data')) {
$counter_key = substr($key, 4);
$counter = $redis->get($counter_key);
if ($counter >= 5){
$ttl = $redis->ttl($key);
$ttl_human = secs_to_str($ttl);
$raw_data = $redis->get($key);
$data = explode("++", $raw_data);
$i = 0;
# We are iterating Redis data: 0-> Date, 1 -> attacker_ip, 2 -> useragent_platform, 3 -> useragent, 4 -> message
$get_os_from_useragent = False;
foreach ($data as $field) {
$field = trim($field);
if ($i == 0) {
$attacker_data[] = $field;
} elseif ($i == 1) {
$attacker_ip = $field;
## We have limits requesting /ip-api.com url so we try to cache it
if ($redis->exists('geoipdata'.$attacker_ip)) {
$geoipdata = ($redis->get('geoipdata'.$attacker_ip));
$attacker_data[] = $geoipdata;
} else {
$ips = array();
$ips[] = $field;
$endpoint = 'http://ip-api.com/batch';
$options = [
'http' => [
'method' => 'POST',
'user_agent' => 'AlfaExploit/1.0',
'header' => 'Content-Type: application/json',
'content' => json_encode($ips)
]
];
if (($response = @file_get_contents($endpoint, false, stream_context_create($options))) === false) {
$attacker_data[] = 'UNKNOWN';
# Cache data: 3600s -> 1h
$redis->set('geoipdata'.$attacker_ip, 'UNKNOWN');
$redis->expire('geoipdata'.$attacker_ip, 3600);
} else {
$array = json_decode($response, true);
$status = $array[0]['status'];
if ($status == 'fail' ){
$attacker_data[] = $array[0]['message'];
# Cache data: 3600s -> 1h
$redis->set('geoipdata'.$attacker_ip, $array[0]['message']);
$redis->expire('geoipdata'.$attacker_ip, 3600);
} else {
$country = $array[0]['country'];
$regionName = $array[0]['regionName'];
$lat = $array[0]['lat'];
$lon = $array[0]['lon'];
$isp = $array[0]['isp'];
$attacker_data[] = $country.'/'.$regionName.'('.$lat.' '.$lon.')'. $isp;
# Cache data: 3600s -> 1h
$redis->set('geoipdata'.$attacker_ip, $country.'/'.$regionName.'('.$lat.' '.$lon.')'. $isp);
$redis->expire('geoipdata'.$attacker_ip, 3600);
}
}
}
} elseif ($i == 2) {
# useragent_platform is NULL, continue, we will try to get it from user-agent
if ($field == 'NULL') {
$get_os_from_useragent = True;
} else {
$attacker_data[] = str_replace('"', '', $field);;
}
} elseif ($i == 3 && $get_os_from_useragent) {
# Try to get OS from user-agent
$attacker_data[] = user_agent_os($field, $os_array);
} elseif ($i == 4) {
$attacker_data[] = $field;
}
$i = $i + 1;
}
# Print table data
echo "<tr>";
# DATE:
echo "<td>$attacker_data[0]</td>";
# IP:
if ($ip_address == $attacker_ip) {
echo "<td><span style=\"color:#E20D41;\">$attacker_ip</span></td>";
} else {
echo "<td>$attacker_ip</td>";
}
# ATTACKER DATA
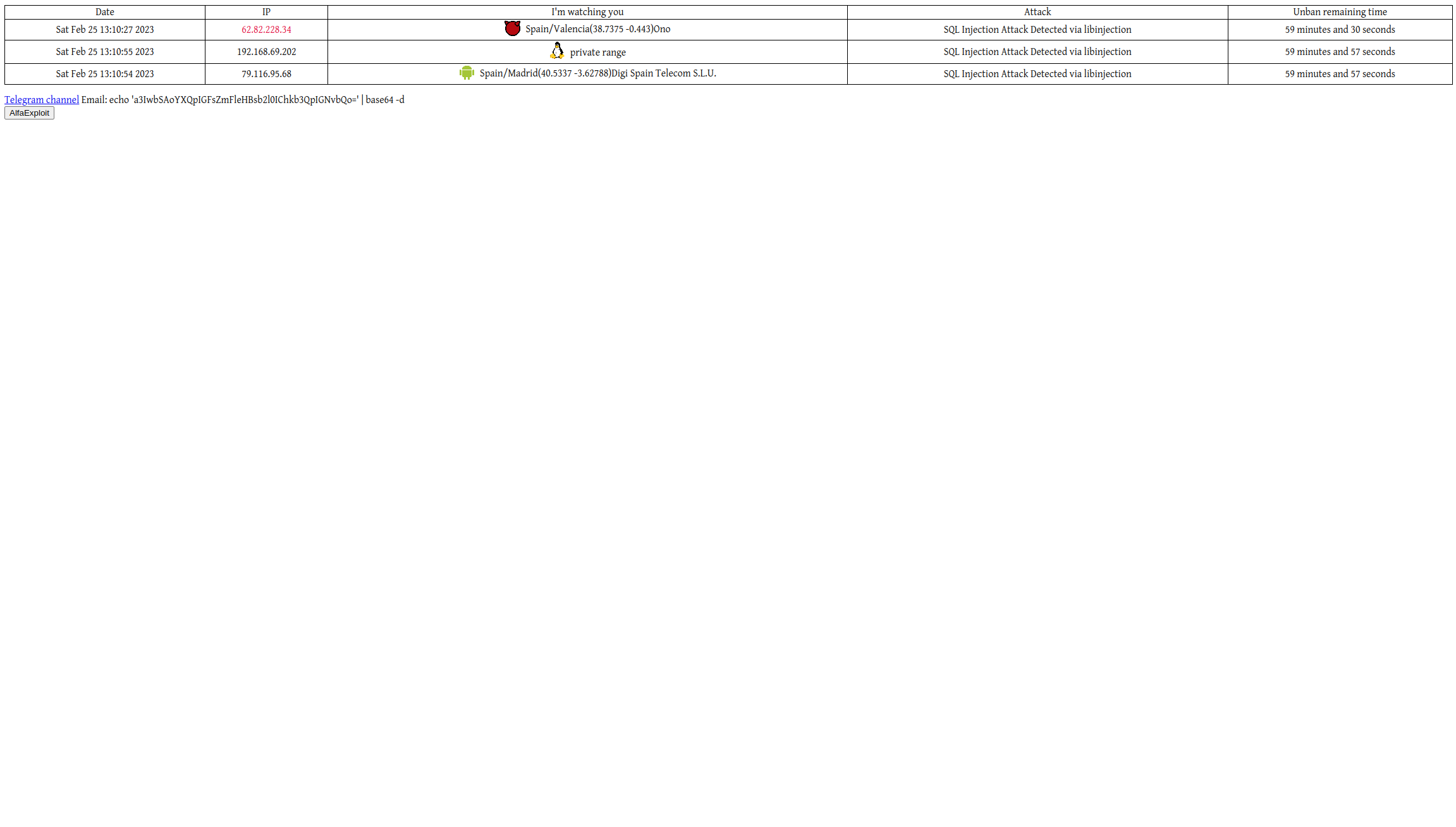
echo "<td><img src=/images/$attacker_data[2].png><span class='attacker_data'>$attacker_data[1]</span></td>";
echo "<td>$attacker_data[3]</td>";
echo "<td>$ttl_human</td>";
echo "</tr>";
}
}
}
echo "</table>";
echo '<a href="https://t.me/AlfaExploia">Telegram channel</a> Email: echo \'a3IwbSAoYXQpIGFsZmFleHBsb2l0IChkb3QpIGNvbQo=\' | base64 -d';
echo '<form action="https://alfaexploit.com">';
echo '<button type="submit">AlfaExploit</button>';
echo '</form>';
echo "</body>";
echo "</html>";
Useful Scripts
This script will allow us to quickly see the banned attackers. This script is designed to be executed on the physical server or if it is a distributed infrastructure in the Ha-Proxy. If we want to run it on the rest of the servers, we just have to delete the lines:
print('')
print('----------------')
print('>> HA-Proxy FILE')
print('----------------')
if os.path.exists(HaProxyBlacklistFile):
HaProxyBlacklist = open(HaProxyBlacklistFile, 'r')
for bannedhost in HaProxyBlacklist.readlines():
bannedhost = bannedhost.replace("\n", "")
print(bannedhost)
print('')
print('----------------')
print('>> HA-Proxy ACL')
print('---------------')
try:
hap = haproxy.HAProxy(socket_dir=HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = True
except:
print('ERRRO: Cant connect to AdminSocket: %s so its impossible to delete attacker IP from blacklist ACL' % HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = False
if canConnectToAdminSocket:
aclCounter = 0
for acl in hap.show_acl():
if acl[0] == '#':
continue
if re.match(BadguysAclPattern, acl):
badguysAclFound = 1
break
aclCounter = aclCounter + 1
if badguysAclFound == 1:
for aclAttackerRaw in hap.show_acl(aclCounter):
aclAttacker = aclAttackerRaw.split(' ')[1]
print(aclAttacker)
#!/usr/local/bin/python
import redis
import os
import subprocess
import re
import time
import datetime
from haproxyadmin import haproxy
HaProxyBlacklistFile = "/usr/local/bastille/jails/Atlas/root/usr/local/etc/bagguys.list"
HaProxyAdminSocketDir = "/usr/local/bastille/jails/Atlas/root/var/run/"
BadguysAclPattern = ".*\(/usr/local/etc/bagguys\.list\) pattern loaded from file '/usr/local/etc/bagguys\.list'.*"
try:
redisconnection = redis.Redis(host="192.168.69.2", port=6379, db=0, password='XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX', charset="utf-8", decode_responses=True)
redisconnection.ping()
except:
print('++ ERROR: Cant connect to redis server')
quit()
print('')
print('---------------')
print('>> REDIS')
print('---------------')
for attacker in redisconnection.scan_iter():
if attacker[0:4] == 'data' or attacker[0:9] == 'geoipdata':
continue
else:
rediscounter = redisconnection.get(attacker)
attackerTTL = redisconnection.ttl(attacker)
remainingTime = str(datetime.timedelta(seconds=attackerTTL))
print("> Attacker: %s Counter: %s" % (attacker, rediscounter))
print("TTL: %s RemainingTime: %s" % (attackerTTL, remainingTime))
if int(rediscounter) >= 5:
print('Banned: YES')
else:
print('Banned: NO')
if redisconnection.get('data' + attacker):
data = redisconnection.get('data' + attacker)
#print("Data: %s" % data)
timestamp = data.split('++')[0]
print("timestamp: %s" % timestamp)
attacker = data.split('++')[1]
#print("attacker: %s" % attacker)
useragent_platform = data.split('++')[2]
print("useragent_platform: %s" % useragent_platform)
useragent = data.split('++')[3]
print("useragent: %s" % useragent)
message = data.split('++')[4]
print("message: %s" % message)
host = data.split('++')[5]
#print("host: %s" % host)
url = data.split('++')[6]
#print("url: %s" % url)
method = data.split('++')[7]
#print("method: %s" % method)
payload = data.split('++')[8]
#print("payload: %s" % payload)
print('')
print('---------------')
print('>> PF')
print('---------------')
bannedhosts = subprocess.run(["pfctl", "-t", "badguys", "-T", "show"], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, text=True)
print("PF Banned hosts: \n%s" % bannedhosts.stdout)
print('')
print('----------------')
print('>> HA-Proxy FILE')
print('----------------')
if os.path.exists(HaProxyBlacklistFile):
HaProxyBlacklist = open(HaProxyBlacklistFile, 'r')
for bannedhost in HaProxyBlacklist.readlines():
bannedhost = bannedhost.replace("\n", "")
print(bannedhost)
print('')
print('----------------')
print('>> HA-Proxy ACL')
print('---------------')
try:
hap = haproxy.HAProxy(socket_dir=HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = True
except:
print('ERRRO: Cant connect to AdminSocket: %s so its impossible to delete attacker IP from blacklist ACL' % HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = False
if canConnectToAdminSocket:
aclCounter = 0
for acl in hap.show_acl():
if acl[0] == '#':
continue
if re.match(BadguysAclPattern, acl):
badguysAclFound = 1
break
aclCounter = aclCounter + 1
if badguysAclFound == 1:
for aclAttackerRaw in hap.show_acl(aclCounter):
aclAttacker = aclAttackerRaw.split(' ')[1]
print(aclAttacker)
We assign the necessary permissions:
When executed, we will see the following output:
---------------
>> REDIS
---------------
> Attacker: 192.168.69.202 Counter: 19
TTL: 3522 RemainingTime: 0:58:42
Banned: YES
timestamp: Sat Feb 25 12:56:26 2023
useragent_platform: "Linux"
useragent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/109.0.0.0 Safari/537.36
message: SQL Injection Attack Detected via libinjection
---------------
>> PF
---------------
PF Banned hosts:
192.168.69.202
----------------
>> HA-Proxy FILE
----------------
192.168.69.202
----------------
>> HA-Proxy ACL
---------------
192.168.69.202
Another really useful script is to flush all bans. This script is designed to be executed on the physical server or if it is a distributed infrastructure in the Ha-Proxy. If we want to run it on the rest of the servers, we just have to delete the lines:
print('')
print('----------------')
print('>> HA-Proxy FILE')
print('----------------')
if os.path.exists(HaProxyBlacklistFile):
try:
open(HaProxyBlacklistFile, 'w').close()
except IOError:
print('Failure')
print('')
print('----------------')
print('>> HA-Proxy ACL')
print('---------------')
try:
hap = haproxy.HAProxy(socket_dir=HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = True
except:
print('ERRRO: Cant connect to AdminSocket: %s so its impossible to delete attacker IP from blacklist ACL' % HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = False
if canConnectToAdminSocket:
aclCounter = 0
for acl in hap.show_acl():
if acl[0] == '#':
continue
if re.match(BadguysAclPattern, acl):
badguysAclFound = 1
break
aclCounter = aclCounter + 1
if badguysAclFound == 1:
for aclAttackerRaw in hap.show_acl(aclCounter):
hap.del_acl(aclCounter, aclAttackerRaw)
#!/usr/local/bin/python
import redis
import os
import subprocess
import re
import datetime
from haproxyadmin import haproxy
HaProxyBlacklistFile = "/usr/local/bastille/jails/Atlas/root/usr/local/etc/bagguys.list"
HaProxyAdminSocketDir = "/usr/local/bastille/jails/Atlas/root/var/run/"
BadguysAclPattern = ".*\(/usr/local/etc/bagguys\.list\) pattern loaded from file '/usr/local/etc/bagguys\.list'.*"
try:
redisconnection = redis.Redis(host="192.168.69.2", port=6379, db=0, password='XXXXXXX', charset="utf-8", decode_responses=True)
redisconnection.ping()
except:
print('++ ERROR: Cant connect to redis server')
quit()
print('')
print('---------------')
print('>> REDIS')
print('---------------')
try:
redisconnection.flushdb()
except:
print('Failure')
print('')
print('---------------')
print('>> PF')
print('---------------')
try:
bannedhosts = subprocess.run(["pfctl", "-t", "badguys", "-T", "flush"], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, text=True)
except:
print('Failure')
print('')
print('----------------')
print('>> HA-Proxy FILE')
print('----------------')
if os.path.exists(HaProxyBlacklistFile):
try:
open(HaProxyBlacklistFile, 'w').close()
except IOError:
print('Failure')
print('')
print('----------------')
print('>> HA-Proxy ACL')
print('---------------')
try:
hap = haproxy.HAProxy(socket_dir=HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = True
except:
print('ERRRO: Cant connect to AdminSocket: %s so its impossible to delete attacker IP from blacklist ACL' % HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = False
if canConnectToAdminSocket:
aclCounter = 0
for acl in hap.show_acl():
if acl[0] == '#':
continue
if re.match(BadguysAclPattern, acl):
badguysAclFound = 1
break
aclCounter = aclCounter + 1
if badguysAclFound == 1:
for aclAttackerRaw in hap.show_acl(aclCounter):
hap.del_acl(aclCounter, aclAttackerRaw)
We assign the necessary permissions:
When executed, we will see the following output:
---------------
>> REDIS
---------------
---------------
>> PF
---------------
1 addresses deleted.
----------------
>> HA-Proxy FILE
----------------
----------------
>> HA-Proxy ACL
---------------
Final Result
The Telegram notifications will look like this:
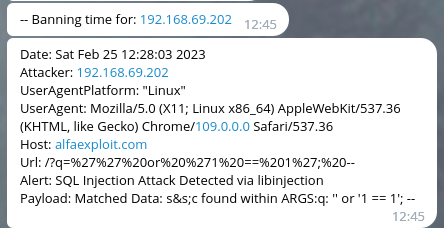
And the dashboard will look like this: