Como ya explicamos en artículos anteriores libmodsecurity es un WAF(Web Application Firewall), este nos permite detectar ciertos tipos de ataques en base a unas reglas predefinidas, mediante estas firmas podremos detectar inyecciones SQL, XSS, LFI, RFI. En esta ocasión vamos a montar un sistema en el que seremos noficiados vía Telegram cuando se detecte un ataque, se aplicarán reglas de PF y se mostrará una web donde se informará del motivo del baneo.
El artículo se divide en varias secciones:
- Compilación de Nginx
- Instalación de libmodsecurity
- Whitelistear URLs
- Deshabilitar reglas
- Limpieza de logs
- Sistema de análisis de logs y baneo
- Instalación de Redis
- Script modsecurityAnalizer.py
- Script modsecurityNotifier.py
- Script modsecurityPF.py
- Reglas de filtrado PF
- Configuración Ha-Proxy
- Dashboard atacantes
- Scripts útiles
- Resultado final
Compilación de Nginx
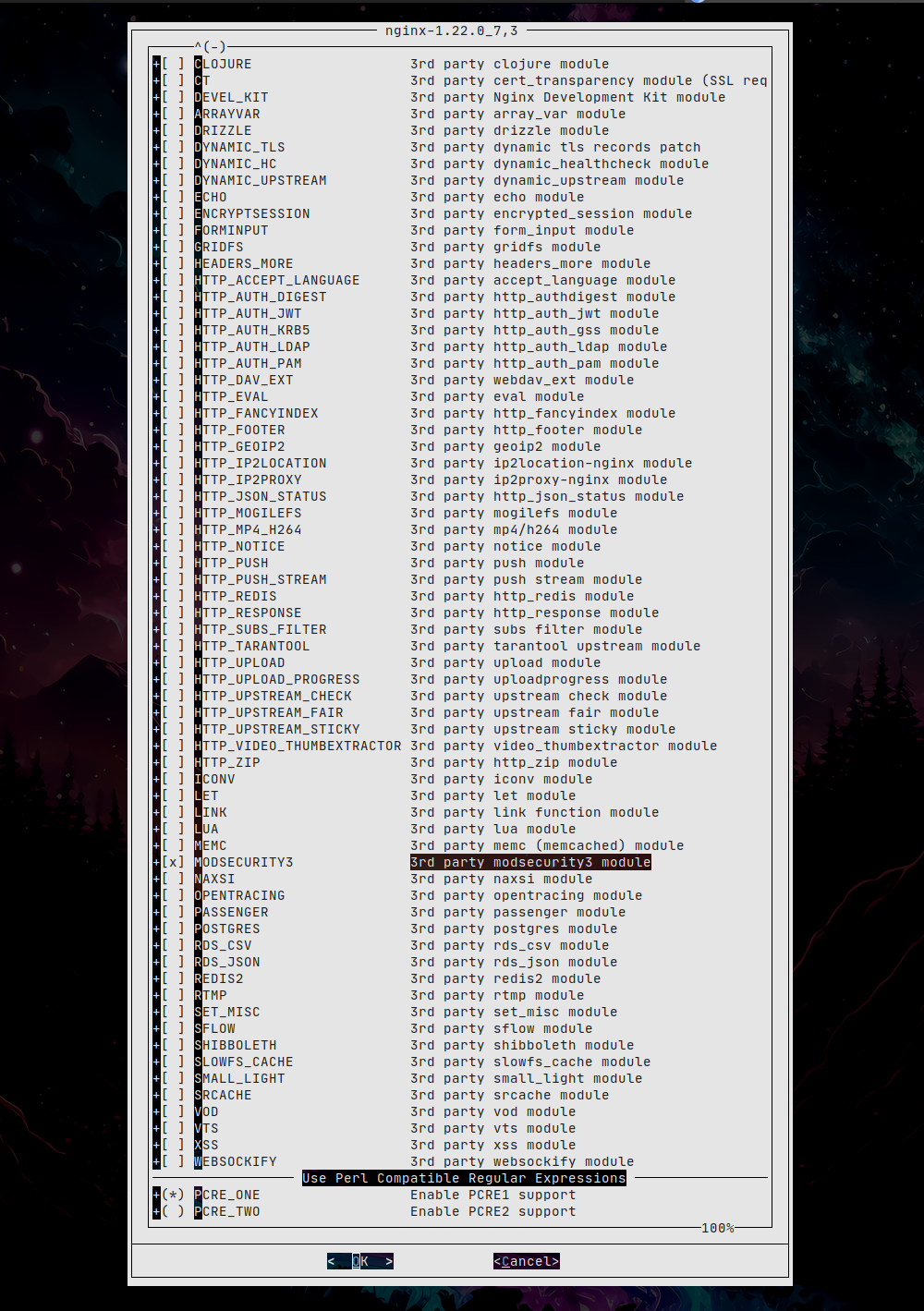
Si ya tenemos instalado Nginx debemos consultar si fué compilado con soporte para libmodsecurity:
MODSECURITY3 : off
NOTA: La versión full(nginx-full) tampoco lleva la opción habilitada.
En versiones anteriores a 03 Jun 2020 18:49:04 Nginx debía ser compilado con soporte para modsecurity3, tener la librería modsecurity3 y además instalar el conector modsecurity3-nginx, en versiones posteriores a dicha fecha si compilamos Nginx con soporte para modsecurity3 ya lleva incorporado el conector, pero debemos añadir la orden de carga del módulo en la configuración de Nginx, en la versión vieja este paso era innecesario.
r537834 | joneum | 2020-06-03 20:49:04 +0200 (Wed, 03 Jun 2020) | 11 lines
Merge r532727 from www/nginx-devel:
Convert the following third-party modules to dynamic:
o) accept_language
o) modsecurity3-nginx
Fix the third-party auth_krb5 module build.
Sponsored by: Netzkommune GmbH
Si instalamos modsecurity3-nginx con la versión nueva de Nginx y cargamos el módulo desde la configuación de Nginx veremos el siguiente error:
2020/06/06 14:46:36 [emerg] 24011#101851: module "/usr/local/libexec/nginx/ngx_http_modsecurity_module.so" is not binary compatible in /usr/local/etc/nginx/nginx.conf:4
Además pkg nos advertirá de que el paquete modsecurity3-nginx y nginx entran en conflicto ya que los dos intentan instalar el mismo conector.
Compilamos mediante ports con las opciones que deseemos, nos aseguramos de habilitar modsecurity3 y recordad que una vez se dá el paso a ports hay que gestionar todos los paquetes desde ports, podéis encontrar mas información en este artículo anterior.
Antes de compilar e intalar Nginx desde los ports desinstalamos la versión actual.
Preparamos el sistema de ports:
cd /usr/ports
make fetchindex
Realizamos una búsqueda:
Port: nginx-1.22.1_5,3
Path: /usr/ports/www/nginx
Info: Robust and small WWW server
Maint: joneum@FreeBSD.org
B-deps: pcre-8.45_3
R-deps: pcre-8.45_3
WWW: https://nginx.com/
Configuramos las opciones:
make config
Compilamos e instalamos:
make install
Limpiamos ficheros temporales:
Instalación de libmodsecurity
Instalamos la librería libmodsecurity:
make config
make
make install
make clean
Nos bajamos las reglas de OWASP:
git clone https://github.com/SpiderLabs/owasp-modsecurity-crs.git
cd owasp-modsecurity-crs
cp crs-setup.conf.example crs-setup.conf
Nos bajamos el fichero de configuración base de libmodsecurity:
cd /usr/local/etc/modsec
fetch https://raw.githubusercontent.com/SpiderLabs/ModSecurity/v3/master/modsecurity.conf-recommended
fetch https://raw.githubusercontent.com/SpiderLabs/ModSecurity/49495f1925a14f74f93cb0ef01172e5abc3e4c55/unicode.mapping
mv modsecurity.conf-recommended modsecurity.conf
Nos aseguramos de tener ciertos parámetros con los valores indicados:
SecRuleEngine On
SecAuditLogFormat json
SecAuditEngine RelevantOnly
SecAuditLog /var/log/modsec_audit.log
Incluimos en la configuración principal el fichero base y las reglas de OWASP:
# Include the recommended configuration
Include /usr/local/etc/modsec/modsecurity.conf
# OWASP CRS v3 rules
Include /usr/local/owasp-modsecurity-crs/crs-setup.conf
Include /usr/local/owasp-modsecurity-crs/rules/*.conf
Habilitamos libmodsecurity en la configuración de Nginx añadiendo como primera línea el load del módulo:
load_module /usr/local/libexec/nginx/ngx_http_modsecurity_module.so;
server {
...
modsecurity on;
modsecurity_rules_file /usr/local/etc/modsec/main.conf;
Reiniciamos el servicio:
Probamos cualquier tipo de ataque, en mi caso una inyección MySQL con el siguiente payload:
' or '1==1'; --
Veremos una entrada nueva en el log y la petición web habrá sido bloqueada con un 403 Forbidden:
Si vamos a generar muchas entradas en el log es preferible escribirlas en formato concurrent, de este modo no se logearán en un fichero de texto de forma serializada, si no que se hará en distintos ficheros de forma paralela:
#SecAuditLogType Serial
SecAuditLogType Concurrent
#SecAuditLog /var/log/modsec_audit.log
SecAuditLogStorageDir /opt/modsecurity/var/audit
Reiniciamos el servicio:
Creamos el directorio donde almacenar las entradas de log:
chown -R www:www /opt/modsecurity/var/audit/
chmod 775 /opt/modsecurity/var/audit/
Instalamos la herramienta jq, esta nos será útil para visualizar la información de los logs de forma mas cómoda:
make config
make
make install
make clean
Consultamos el campo message de una de las entradas:
"SQL Injection Attack Detected via libinjection"
"Inbound Anomaly Score Exceeded (Total Score: 5)"
NOTA: No es necsario filtrar si queremos ver la información completa simplemente empipamos la salida del cat a un jq sin parámetros.
Whitelistear URLs
Si en nuestra aplicación web hay alguna funcionalidad que requiera un comportamiento un poco fuera de lo normal podemos whitelistearla para que las reglas no salten cuando se trate de esa sección:
vi /usr/local/owasp-modsecurity-crs/rules/REQUEST-900-EXCLUSION-RULES-BEFORE-CRS.conf
SecRule REQUEST_URI "@beginsWith /CUSTOM_WEB_PATH" \
"id:1001,\
phase:1,\
pass,\
nolog,\
ctl:ruleEngine=Off"
Deshabilitar reglas
Si por otro lado queremos deshabilitar alguna regla en concreto podemos utilizar la directiva SecRuleRemoveById
NOTA : Esta directiva debe ser especificada después de la regla que se esté deshabilitando.
En mi caso estaba teniendo problemas con la regla:
CGI source code leakage
"ruleId": "950140",
"file": "/usr/local/owasp-modsecurity-crs/rules/RESPONSE-950-DATA-LEAKAGES.conf",
"lineNumber": "66",
Al mostrar código por la web la alarma salta por pensar que se está filtrando código fuente de la propia página, añadimos el fichero de reglas deshabilitadas:
# Include the recommended configuration
Include /usr/local/etc/modsec/modsecurity.conf
# OWASP CRS v3 rules
Include /usr/local/owasp-modsecurity-crs/crs-setup.conf
Include /usr/local/owasp-modsecurity-crs/rules/*.conf
# Disabled rules
Include /usr/local/etc/modsec/disabledRules.conf
Indicamos que regla deshabilitar:
SecRuleRemoveById 950140
En cambio si queremos deshabilitarla solo para una IP(necesario si habilitamos el check en un Ha-Proxy):
SecRule REMOTE_ADDR "@ipMatch IP_ADDRESS" "id:1,phase:1,t:none,nolog,pass,ctl:ruleRemoveById=920280"
Limpieza de logs
Una buena idea es eliminar los logs de libmodsecurity cada X tiempo, para ello yo tengo el siguiente CRON habilitado:
00 11 * * * /bin/rm -rf /usr/local/bastille/jails/MetaCortex/root/opt/modsecurity/var/audit/* >/dev/null 2>&1
Sistema de análisis de logs y baneo
El sistema se compone de un servidor Redis y varios scripts en Python:
- Script de análisis de logs de libmodsecurity: modsecurityAnalizer.py
- Script de notificación via Telegram, baneo mediante PF y configuración de ACLs y listas en Ha-Proxy: modsecurityNotifier.py
- Script de baneo mediante PF: modsecurityPF.py
Según nuestra topología los scripts se ejecutarán en un servidor determinado u otro, en mi caso todos los servicios están montados en un mismo servidor físico por lo tanto ejecutaré los scripts modsecurityAnalizer.py y modsecurityNotifier.py en este ya que al bloquear por PF estaré filtrando para todos los servidores de forma simultánea.
En caso de tener una infraestructura mas distribuida deberemos ejecutar modsecurityAnalizer.py en el Nginx donde se reciben los ataques, modsecurityNotifier.py en el Ha-Proxy y modsecurityPF.py en el resto de servidores que queramos proteger.
| Todos los servicios en el mismo host padre | Servicios separadaos |
|---|---|
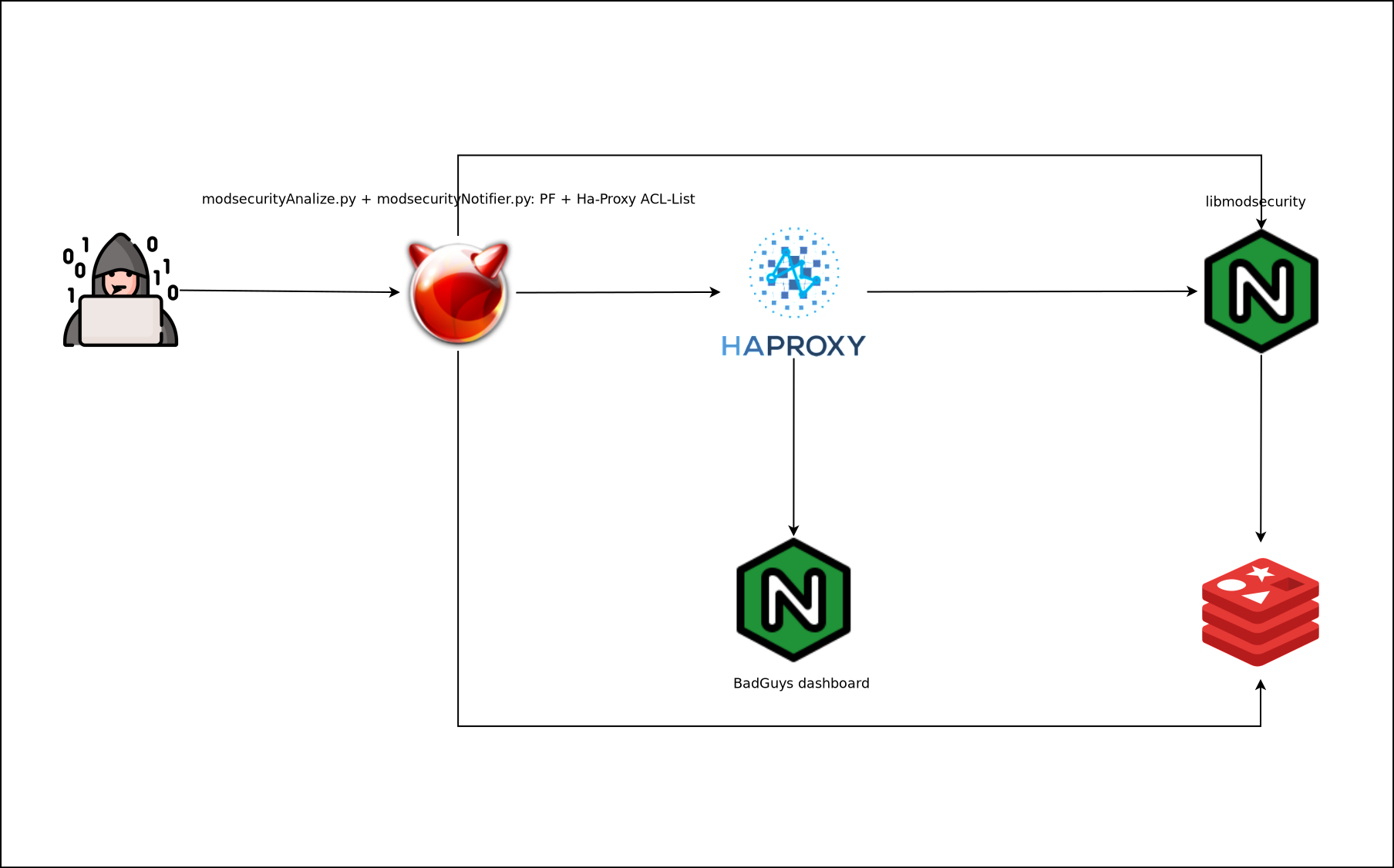
|
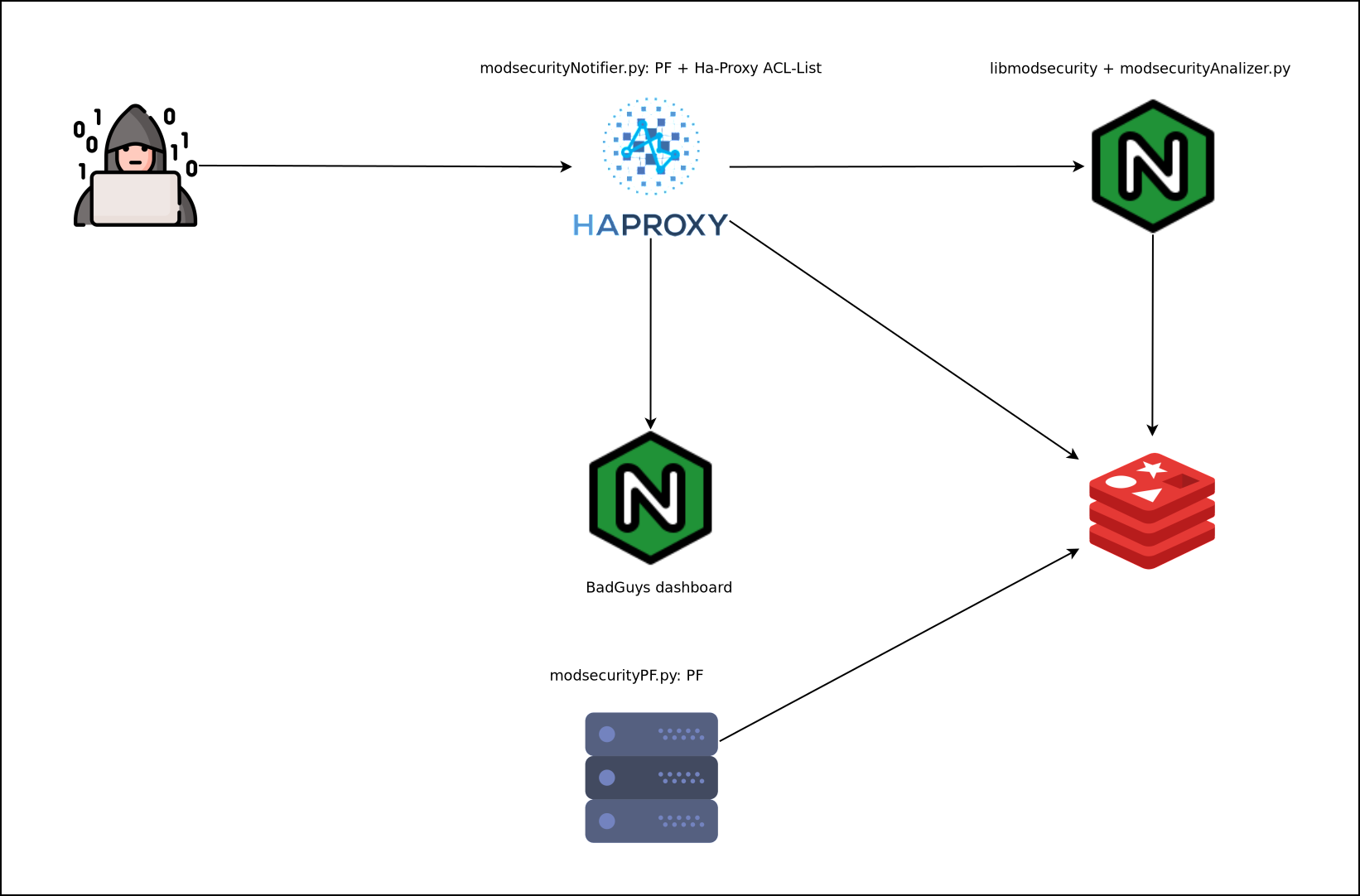
|
Los pasos de baneo de ataques son:
- Generar logs mediante libmodsecurity en el servidor Nginx.
- Leer desde el servidor padre o el servidor Nginx dichos logs e insertar dicha información en Redis.
- Leer desde el servidor padre o el Ha-Proxy los datos del Redis y configurar las reglas de PF , además mantendremos sincronizados una ACL y un fichero lista de Ha-Proxy.
- El Ha-Proxy envía los atacantes que macheen la ACL “badguys” a un backend especial.
- Se atiende a los atacantes con una app web donde se muestra información del atacante, el motivo y el tiempo restante de baneo.
- Si la infraestructura es distribuida ejecutaremos en el resto de servidores el script modsecurityPF.py que simplemente leerá del Redis y aplicará reglas de PF.
Instalación de Redis
Para que los distintos scripts puedan comunicarse, instalaremos un servidor Redis:
Lo bindeamos a su ip y asignamos un password:
bind 192.168.69.2
requirepass XXXXXXXXXX
Habilitamos y arrancamos el servicio:
service redis start
Consultamos el estado del redis:
# Server
redis_version:7.0.8
redis_git_sha1:00000000
redis_git_dirty:0
redis_build_id:8e3f49544e856f48
redis_mode:standalone
os:FreeBSD 13.1-RELEASE-p5 amd64
.......
Script modsecurityAnalizer.py
Mediante este script analizaremos los logs generados por libmodsecurity y generaremos las keys asociadas en Redis.
#!/usr/local/bin/python
import sys
import time
from datetime import timedelta
import os
import json
import requests
import redis
from watchdog.observers import Observer
from watchdog.events import FileSystemEventHandler
apikey = "XXXXXXXXXX"
telegramurl = "https://api.telegram.org/bot{}/sendMessage".format(apikey)
userid = "XXXXXXXXXX"
haproxy_ip = '192.168.69.19'
try:
redisconnection = redis.Redis(host="192.168.69.2", port=6379, db=0, password='XXXXXXXXXX')
redisconnection.ping()
except:
print('++ ERROR: Cant connect to redis server')
msg = 'ERROR ' + os.uname().nodename + '(modsecurityAnalizer.py): Cant connect to redis server'
data = {"chat_id":userid, "text":msg}
try:
r = requests.post(telegramurl,json=data)
except:
print("++ Error sending telegram message")
quit()
print("-- Ready to process log files")
class EventHandler(FileSystemEventHandler):
def on_any_event(self, event):
#print("Event type: %s" % event.event_type)
#print("Event file: %s" % event.src_path)
if event.event_type == 'created':
if os.path.isfile(event.src_path):
print('')
print('------------------------------------------------')
print("Processing: %s" % event.src_path)
with open(event.src_path) as fp:
for line in fp:
#print('INSIDE LOOP1: Log lines')
try:
rawdata = json.loads(line)
except:
print('Exception happened loading json data')
continue
for messageline in rawdata['transaction']['messages']:
#print('INSIDE LOOP2: messages')
message = messageline['message']
# Each alert generates two messages one of the real alert another with 'Out/In bound Anomaly Score Exceeded (Total Score: 5)'
if message == 'Outbound Anomaly Score Exceeded (Total Score: 5)' or message == 'Inbound Anomaly Score Exceeded (Total Score: 5)':
continue
print('=====================================')
#print('Message: %s' % message)
data = messageline['details']['data']
#print('data: %s' % data)
# Delete not matched rules messages and anomaly score checks
if message != "":
try:
timestamp = rawdata['transaction']['time_stamp']
except:
timestamp = 'NULL'
try:
attacker = rawdata['transaction']['request']['headers']['x-forwarded-for']
except:
attacker = rawdata['transaction']['client_ip']
if attacker == haproxy_ip:
continue
#attacker = 'NULL'
try:
useragent_platform = rawdata['transaction']['request']['headers']['sec-ch-ua-platform']
except:
useragent_platform = 'NULL'
try:
useragent = rawdata['transaction']['request']['headers']['user-agent']
except:
useragent = 'NULL'
try:
host = rawdata['transaction']['request']['headers']['host']
except:
host = 'NULL'
try:
url = rawdata['transaction']['request']['uri']
except:
url = 'NULL'
try:
method = rawdata['transaction']['request']['method']
except:
method = 'NULL'
try:
payload = messageline['details']['data']
except:
payload = 'NULL'
print('')
print(">> Timestamp: %s" % timestamp)
print("Attacker: %s" % attacker)
print("UserAgentPlatform: %s" % useragent_platform)
print("UserAgent: %s" % useragent)
print("Message: %s" % message)
print("Host: %s" % host)
print("URL: %s" % url)
print("Method: %s" % method)
#print("Payload: %s" % payload)
print(">> Checking redis IP: %s" % attacker)
print("Incrementing redis key value for IP: %s" % attacker)
if redisconnection.get(attacker):
redisconnection.incr(attacker)
else:
redisconnection.incr(attacker)
redisconnection.expire(attacker, timedelta(seconds=3600))
rediscounter = redisconnection.get(attacker)
print("rediscounter: %s" % rediscounter)
print(">> Filling attacker data")
datastring = timestamp + '++' + attacker + '++' + useragent_platform + '++' + useragent + '++' + message + '++' + host + '++' + url + '++' + method + '++' + payload
redisconnection.set('data' + attacker, datastring)
redisconnection.expire('data' + attacker, timedelta(seconds=3600))
db_datastring = redisconnection.get('data' + attacker)
#print("- datastring: %s" % datastring)
#print("- db_datastring: %s" % db_datastring)
print(">> Done")
if __name__ == "__main__":
path = '/usr/local/bastille/jails/MetaCortex/root/opt/modsecurity/var/audit/'
event_handler = EventHandler()
observer = Observer()
observer.schedule(event_handler, path, recursive=True)
observer.start()
try:
while True:
time.sleep(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
observer.stop()
observer.join()
Le damos permisos de ejecución:
El script RC de gestión del servicio quedaría del siguiente modo:
#!/bin/sh
#
# PROVIDE: modsecurityAnalizer
# REQUIRE: DAEMON
# KEYWORD: shutdown
. /etc/rc.subr
name=modsecurityAnalizer
rcvar=modsecurityAnalizer_enable
command="/root/.scripts/modsecurityAnalizer.py"
start_cmd="modsecurityAnalizer_start"
stop_cmd="${name}_stop"
status_cmd="${name}_status"
pidfile="/var/run/${name}.pid"
modsecurityAnalizer_start(){
echo "Starting service: ${name}."
/usr/sbin/daemon -c -f -p ${pidfile} ${command}
}
modsecurityAnalizer_stop(){
if [ -f ${pidfile} ]; then
echo "Stopping service: ${name}"
kill -s TERM $(cat ${pidfile})
sleep 3
else
echo "It appears ${name} is not running."
fi
}
modsecurityAnalizer_status(){
if [ -f ${pidfile} ]; then
echo "${name} running with PID: $(cat ${pidfile})"
else
echo "It appears ${name} is not running."
fi
}
load_rc_config $name
run_rc_command "$1"
Asignamos permisos:
chown root:wheel /usr/local/etc/rc.d/modsecurityAnalizer
Habilitamos el servicio y lo arrancamos:
service modsecurityAnalizer start
Script modsecurityNotifier.py
Este script consultará el Redis, avisará vía Telegram de los ataques recibidos, configurará reglas PF y mantendrá una ACL y una lista de Ha-Proxy con las ips de los atacantes.
La razón por la que configuraremos ACLs y listas simultáneamente es porque las ACLs se insertarán por SocketAdmin de Ha-Proxy, al reiniciar el Ha-Proxy las ACLs desaparecen, para evitar esto mantendremos también la lista /usr/local/etc/bagguys.list de este modo en caso de reinicio la lista contendrá las mismas ips que habían en la ACL.
#!/usr/local/bin/python
import redis
import requests
import subprocess
import time
import os
import re
from haproxyadmin import haproxy
apikey = "XXXXXXXXXX"
telegramurl = "https://api.telegram.org/bot{}/sendMessage".format(apikey)
userid = "XXXXXXXXXX"
HaProxyBlacklistFile = "/usr/local/bastille/jails/Atlas/root/usr/local/etc/bagguys.list"
HaProxyAdminSocketDir = "/usr/local/bastille/jails/Atlas/root/var/run/"
BadguysAclPattern = ".*\(/usr/local/etc/bagguys\.list\) pattern loaded from file '/usr/local/etc/bagguys\.list'.*"
try:
redisconnection = redis.Redis(host="192.168.69.2", port=6379, db=0, password='XXXXXXXXXX', charset="utf-8", decode_responses=True)
redisconnection.ping()
except:
print('++ ERROR: Cant connect to redis server')
msg = 'ERROR ' + os.uname().nodename + '(modsecurityNotifier.py): Cant connect to redis server'
data = {"chat_id":userid, "text":msg}
try:
r = requests.post(telegramurl,json=data)
except:
print("++ Error sending telegram message")
quit()
while(True):
print('')
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('>> Checking REDIS content')
print('------------------------------------------------')
for attacker in redisconnection.scan_iter():
#print("-- Analyzing key: %s" % attacker)
if attacker[0:4] == 'data' or attacker[0:9] == 'geoipdata':
continue
else:
rediscounter = redisconnection.get(attacker)
print("Attacker: %s Counter: %s" % (attacker, rediscounter))
if int(rediscounter) >= 5 and redisconnection.get('data' + attacker):
data = redisconnection.get('data' + attacker)
#print("Data: %s" % data)
timestamp = data.split('++')[0]
print("timestamp: %s" % timestamp)
attacker = data.split('++')[1]
print("attacker: %s" % attacker)
useragent_platform = data.split('++')[2]
print("useragent_platform: %s" % useragent_platform)
useragent = data.split('++')[3]
print("useragent: %s" % useragent)
message = data.split('++')[4]
print("message: %s" % message)
host = data.split('++')[5]
print("host: %s" % host)
url = data.split('++')[6]
print("url: %s" % url)
method = data.split('++')[7]
print("method: %s" % method)
payload = data.split('++')[8]
#print("payload: %s" % payload)
print('------------------------------------------------')
print(">> Trying to ban attacker ip readed from Redis: %s" % attacker)
print('------------------------------------------------')
bannedhosts = subprocess.run(["pfctl", "-t", "badguys", "-T", "show"], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, text=True)
print("PF Banned hosts: \n%s" % bannedhosts.stdout)
blockattacker = 1
for bannedhost in bannedhosts.stdout.split(' '):
bannedhost = bannedhost.replace("\n", "")
if bannedhost == '':
continue
print("Comparing Redis:%s --> PF:%s" % (attacker, bannedhost))
if attacker == bannedhost:
print("Attacker already banned, aborting")
blockattacker = 0
break
#print("blockattacker var value: %s" % blockattacker)
if blockattacker == 1:
print("-- Banning time for: %s" % attacker)
cmd = '/sbin/pfctl -t badguys -T add ' + attacker
cmdreturnvalue = subprocess.call(cmd, shell=True)
print("cmdreturnvalue: %s" % cmdreturnvalue)
if cmdreturnvalue != 0:
print("++ ERROR: Cant add attacker ip to PF badguys table")
print("-- Killing established connections: %s" % attacker)
cmd = '/sbin/pfctl -k ' + attacker
cmdreturnvalue = subprocess.call(cmd, shell=True)
print("cmdreturnvalue: %s" % cmdreturnvalue)
if cmdreturnvalue != 0:
print("++ ERROR: Cant kill established connections")
print('-- Adding to HA-Proxy badguys blacklist file')
HaProxyBlacklist = open(HaProxyBlacklistFile, "a")
HaProxyBlacklist.write(attacker+"\n")
HaProxyBlacklist.close()
print('-- Adding to HA-Proxy ACL via AdminSocket')
try:
hap = haproxy.HAProxy(socket_dir=HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = True
except:
print('ERRRO: Cant connect to AdminSocket: %S so its impossible to add attacker IP to blacklist ACL' % HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = False
if canConnectToAdminSocket:
aclCounter = 0
badguysAclFound = 0
for acl in hap.show_acl():
if acl[0] == '#':
continue
#print("ACL: %s" % acl)
#print("Content: %s" % hap.show_acl(aclCounter))
#print("Comparing ACL: %s -> RegExp: %s" % (acl,BadguysAclPattern))
if re.match(BadguysAclPattern, acl):
print("> MATCH - BadGuys Acl: %s" % aclCounter)
badguysAclFound = 1
break
aclCounter = aclCounter + 1
if badguysAclFound == 1:
print('Current Content: %s' % hap.show_acl(aclCounter))
hap.add_acl(aclCounter, attacker)
print('Post ADD Content: %s' % hap.show_acl(aclCounter))
else:
print('>> ERROR: Cant locate ACL so its impossible to add attacker IP to blacklist')
msg = "-- Banning time for: " + attacker
data = {"chat_id":userid, "text":msg}
try:
r = requests.post(telegramurl,json=data)
except:
print("++ Error sending telegram message")
continue
print("-- Sending telegram alert")
msg = 'Date: ' + str(timestamp) + '\nAttacker: ' + str(attacker) + '\nUserAgentPlatform: ' + str(useragent_platform) + '\nUserAgent: ' + str(useragent) + '\nHost: ' + str(host) + '\nUrl: ' + str(url) + '\nAlert: ' + str(message) + '\nPayload: ' + str(payload)
data = {"chat_id":userid, "text":msg}
try:
r = requests.post(telegramurl,json=data)
except:
print("++ Error sending telegram message")
continue
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('')
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('>> Clearing old PF ips')
print('------------------------------------------------')
bannedhosts = subprocess.run(["pfctl", "-t", "badguys", "-T", "show"], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, text=True)
for bannedhost in bannedhosts.stdout.split(' '):
bannedhost = bannedhost.replace("\n", "")
if bannedhost == '':
continue
redis_found = False
for attacker in redisconnection.scan_iter():
if attacker[0:4] == 'data' or attacker[0:9] == 'geoipdata':
continue
else:
print("Comparing PF:%s --> Redis:%s" % (bannedhost, attacker))
if bannedhost == attacker:
redis_found = True
break
if redis_found == False:
print('-- Unbaning: %s' % bannedhost)
cmd = '/sbin/pfctl -t badguys -T delete ' + bannedhost
cmdreturnvalue = subprocess.call(cmd, shell=True)
print("cmdreturnvalue: %s" % cmdreturnvalue)
if cmdreturnvalue != 0:
print("++ ERROR: Cant unban attacker ip from PF badguys table")
else:
print('Attacker already present in Redis, preserving banning: %s' % bannedhost)
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('')
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('>> Clearing old blacklisted HA-Proxy file')
print('------------------------------------------------')
if os.path.exists(HaProxyBlacklistFile):
bannedhosts = []
HaProxyBlacklist = open(HaProxyBlacklistFile, 'r')
for bannedhost in HaProxyBlacklist.readlines():
bannedhost = bannedhost.replace("\n", "")
#print(bannedhost)
redis_found = False
for attacker in redisconnection.scan_iter():
if attacker[0:4] == 'data' or attacker[0:9] == 'geoipdata':
continue
else:
print("Comparing HA:%s --> Redis:%s" % (bannedhost, attacker))
if bannedhost == attacker:
redis_found = True
break
if redis_found == False:
print('-- Unblacklisting: %s' % bannedhost)
else:
print('Attacker already present in Redis, preserving blacklisting: %s' % bannedhost)
bannedhosts.append(bannedhost)
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('bannedhosts: %s' % bannedhosts)
with open(HaProxyBlacklistFile, 'w') as HaProxyBlacklist:
for bannedhost in bannedhosts:
HaProxyBlacklist.write(bannedhost+'\n')
print('')
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('>> Clearing old blacklisted HA-Proxy ACL')
print('------------------------------------------------')
try:
hap = haproxy.HAProxy(socket_dir=HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = True
except:
print('ERRRO: Cant connect to AdminSocket: %s so its impossible to delete attacker IP from blacklist ACL' % HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = False
if canConnectToAdminSocket:
aclCounter = 0
badguysAclFound = 0
for acl in hap.show_acl():
if acl[0] == '#':
continue
if re.match(BadguysAclPattern, acl):
print("> MATCH - BadGuys Acl: %s" % aclCounter)
badguysAclFound = 1
break
aclCounter = aclCounter + 1
if badguysAclFound == 1:
print('Current Content: %s' % hap.show_acl(aclCounter))
for aclAttackerRaw in hap.show_acl(aclCounter):
aclAttacker = aclAttackerRaw.split(' ')[1]
redis_found = False
for attacker in redisconnection.scan_iter():
if attacker[0:4] == 'data' or attacker[0:9] == 'geoipdata':
continue
else:
print("Comparing ACL:%s --> Redis:%s" % (aclAttacker, attacker))
if aclAttacker == attacker:
redis_found = True
break
if redis_found == False:
print('-- Unblacklisting: %s' % aclAttacker)
hap.del_acl(aclCounter, aclAttackerRaw)
print('Post DEL Content: %s' % hap.show_acl(aclCounter))
else:
print('Attacker already present in Redis, preserving blacklisting: %s' % aclAttacker)
print('------------------------------------------------')
else:
print('>> ERROR: Cant locate ACL so its impossible to del attacker IP from blacklist')
time.sleep(5)
Le damos permisos de ejecución:
El script RC de gestión del servicio quedaría del siguiente modo:
#!/bin/sh
#
# PROVIDE: modsecurityNotifier
# REQUIRE: DAEMON
# KEYWORD: shutdown
. /etc/rc.subr
name=modsecurityNotifier
rcvar=modsecurityNotifier_enable
command="/root/.scripts/modsecurityNotifier.py"
start_cmd="modsecurityNotifier_start"
stop_cmd="modsecurityNotifier_stop"
status_cmd="modsecurityNotifier_status"
pidfile="/var/run/${name}.pid"
modsecurityNotifier_start(){
echo "Starting service: ${name}."
/usr/sbin/daemon -c -f -p ${pidfile} ${command}
}
modsecurityNotifier_stop(){
if [ -f ${pidfile} ]; then
echo "Stopping service: ${name}"
kill -s INT $(cat ${pidfile})
sleep 3
else
echo "It appears ${name} is not running."
fi
}
modsecurityNotifier_status(){
if [ -f ${pidfile} ]; then
echo "${name} running with PID: $(cat ${pidfile})"
else
echo "It appears ${name} is not running."
fi
}
load_rc_config $name
run_rc_command "$1"
Asignamos permisos:
chown root:wheel /usr/local/etc/rc.d/modsecurityNotifier
Habilitamos y arrancamos el servicio:
service modsecurityNotifier start
Script modsecurityPF.py
El siguiente script solo lo utilizaremos si tenemos una infraestructura distribuida, lo ejecutaremos en el resto de servidores que no dependan del Ha-Proxy por ejemplo servidores web, bases de datos, etc.
#!/usr/local/bin/python
import redis
import subprocess
import time
import os
apikey = "XXXXXXXXXX"
telegramurl = "https://api.telegram.org/bot{}/sendMessage".format(apikey)
userid = "XXXXXXXXXX"
try:
redisconnection = redis.Redis(host="192.168.69.2", port=6379, db=0, password='XXXXXXXXXX', charset="utf-8", decode_responses=True)
redisconnection.ping()
except:
print('++ ERROR: Cant connect to redis server')
msg = 'ERROR ' + os.uname().nodename + '(modsecurityPF.py): Cant connect to redis server'
data = {"chat_id":userid, "text":msg}
try:
r = requests.post(telegramurl,json=data)
except:
print("++ Error sending telegram message")
quit()
while(True):
print('')
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('>> Checking REDIS content')
print('------------------------------------------------')
for attacker in redisconnection.scan_iter():
#print("-- Analyzing key: %s" % attacker)
if attacker[0:4] == 'data' or attacker[0:9] == 'geoipdata':
continue
else:
rediscounter = redisconnection.get(attacker)
print("Attacker: %s Counter: %s" % (attacker, rediscounter))
if int(rediscounter) >= 5 and redisconnection.get('data' + attacker):
data = redisconnection.get('data' + attacker)
#print("Data: %s" % data)
timestamp = data.split('++')[0]
print("timestamp: %s" % timestamp)
attacker = data.split('++')[1]
print("attacker: %s" % attacker)
useragent = data.split('++')[2]
print("useragent: %s" % useragent)
message = data.split('++')[3]
print("message: %s" % message)
host = data.split('++')[4]
print("host: %s" % host)
url = data.split('++')[5]
print("url: %s" % url)
method = data.split('++')[6]
print("method: %s" % method)
payload = data.split('++')[7]
#print("payload: %s" % payload)
print('------------------------------------------------')
print(">> Trying to ban attacker ip readed from Redis: %s" % attacker)
print('------------------------------------------------')
bannedhosts = subprocess.run(["pfctl", "-t", "badguys", "-T", "show"], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, text=True)
print("PF Banned hosts: \n%s" % bannedhosts.stdout)
blockattacker = 1
for bannedhost in bannedhosts.stdout.split(' '):
bannedhost = bannedhost.replace("\n", "")
if bannedhost == '':
continue
print("Comparing Redis:%s --> PF:%s" % (attacker, bannedhost))
if attacker == bannedhost:
print("Attacker already banned, aborting")
blockattacker = 0
break
#print("blockattacker var value: %s" % blockattacker)
if blockattacker == 1:
print("-- Banning time for: %s" % attacker)
cmd = '/sbin/pfctl -t badguys -T add ' + attacker
cmdreturnvalue = subprocess.call(cmd, shell=True)
print("cmdreturnvalue: %s" % cmdreturnvalue)
if cmdreturnvalue != 0:
print("++ ERROR: Cant add attacker ip to PF badguys table")
print("-- Killing established connections: %s" % attacker)
cmd = '/sbin/pfctl -k ' + attacker
cmdreturnvalue = subprocess.call(cmd, shell=True)
print("cmdreturnvalue: %s" % cmdreturnvalue)
if cmdreturnvalue != 0:
print("++ ERROR: Cant kill established connections")
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('')
print('------------------------------------------------')
print('>> Clearing old PF ips')
print('------------------------------------------------')
bannedhosts = subprocess.run(["pfctl", "-t", "badguys", "-T", "show"], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, text=True)
for bannedhost in bannedhosts.stdout.split(' '):
bannedhost = bannedhost.replace("\n", "")
if bannedhost == '':
continue
redis_found = False
for attacker in redisconnection.scan_iter():
if attacker[0:4] == 'data' or attacker[0:9] == 'geoipdata':
continue
else:
print("Comparing PF:%s --> Redis:%s" % (bannedhost, attacker))
if bannedhost == attacker:
redis_found = True
break
if redis_found == False:
print('-- Unbaning: %s' % bannedhost)
cmd = '/sbin/pfctl -t badguys -T delete ' + bannedhost
cmdreturnvalue = subprocess.call(cmd, shell=True)
print("cmdreturnvalue: %s" % cmdreturnvalue)
if cmdreturnvalue != 0:
print("++ ERROR: Cant unban attacker ip from PF badguys table")
else:
print('Attacker already present in Redis, preserving banning: %s' % bannedhost)
print('------------------------------------------------')
time.sleep(5)
Le damos permisos de ejecución:
El script RC de gestión del servicio quedaría del siguiente modo:
#!/bin/sh
#
# PROVIDE: modsecurityPF
# REQUIRE: DAEMON
# KEYWORD: shutdown
. /etc/rc.subr
name=modsecurityPF
rcvar=modsecurityPF_enable
command="/root/.scripts/modsecurityPF.py"
start_cmd="modsecurityPF_start"
stop_cmd="modsecurityPF_stop"
status_cmd="modsecurityPF_status"
pidfile="/var/run/${name}.pid"
modsecurityPF_start(){
echo "Starting service: ${name}."
/usr/sbin/daemon -c -f -p ${pidfile} ${command}
}
modsecurityPF_stop(){
if [ -f ${pidfile} ]; then
echo "Stopping service: ${name}"
kill -s INT $(cat ${pidfile})
sleep 3
else
echo "It appears ${name} is not running."
fi
}
modsecurityPF_status(){
if [ -f ${pidfile} ]; then
echo "${name} running with PID: $(cat ${pidfile})"
else
echo "It appears ${name} is not running."
fi
}
load_rc_config $name
run_rc_command "$1"
Asignamos permisos:
chown root:wheel /usr/local/etc/rc.d/modsecurityPF
Habilitamos y arrancamos el servicio:
service modsecurityPF start
Reglas de filtrado PF
Para bloquear el tráfico desde PF utilizaremos una tabla llamada badguys, todo el tráfico proveniente de estas ips será bloqueado con la excepción del puerto 80/443 si se trata del Ha-Proxy en el resto de servidores sería exactamente igual pero eliminando las líneas:
# Continue attending badguys in HA-Proxy, we have a surprise for them:
pass in quick proto tcp from <badguys> to 192.168.69.19 port 80
pass in quick proto tcp from <badguys> to 192.168.69.19 port 443
ext_if = "nfe0"
set block-policy return
scrub in on $ext_if all fragment reassemble
set skip on lo
table <badguys> persist
table <jails> persist
nat on $ext_if from <jails> to any -> ($ext_if:0)
rdr-anchor "rdr/*"
antispoof for $ext_if inet
block log all
pass out quick
pass in proto tcp to 192.168.69.2 port 7777
# SMTP -> HellStorm
pass in proto tcp to 192.168.69.17 port 25
# HTTP/HTTPS -> Atlas
pass in proto tcp to 192.168.69.19 port 80
pass in proto tcp to 192.168.69.19 port 443
# Continue attending badguys in HA-Proxy, we have a surprise for them:
pass in quick proto tcp from <badguys> to 192.168.69.19 port 80
pass in quick proto tcp from <badguys> to 192.168.69.19 port 443
# Xbox -> Paradox
pass in proto tcp from 192.168.69.196 to 192.168.69.18 port 80
# TARS -> Paradox
pass in proto tcp from 192.168.69.198 to 192.168.69.18 port 80
# Garrus -> Paradox, testing purpose
pass in proto tcp from 192.168.69.4 to 192.168.69.18 port 80
pass in proto tcp to any port 22
# Block all traffic from badguys, except 80,443 that was allowed previously:
block in from <badguys>
Configuración Ha-Proxy
Como ya hemos comentado, la idea es mantener sincronizadas las ACLs de HA-Proxy en running-config utilizando el AdminSocket y una lista de ips en un fichero en el sistema de ficheros, de este modo si se reinicia el Ha-Proxy todo seguirá funcionando, ya que leerá el fichero que también tiene la lista de ips.
La configuración del Ha-Proxy quedaría del siguiente modo:
global
daemon
maxconn 5000
log 192.168.69.19:514 local1
user nobody
group nobody
stats socket /var/run/haproxy.sock user nobody group nobody mode 660 level admin
ssl-default-bind-ciphers ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
ssl-default-bind-options ssl-min-ver TLSv1.2 no-tls-tickets
defaults
timeout connect 10s
timeout client 30s
timeout server 30s
mode http
# ENABLE LOGGING:
# TCP connections
#log global
# Backend connections
#option httplog
listen stats
bind *:8404
stats enable
stats uri /stats
stats refresh 5s
stats auth kr0m:8XEn3EL1aYIeKI
frontend HTTP
bind :80
# Allow LetsEncrypt certificate renew and redirect to HTTPS all other requests:
acl letsencrypt path_beg /.well-known/acme-challenge/
http-request redirect scheme https unless letsencrypt
use_backend letsencrypt-backend if letsencrypt
frontend HTTP-SSL
bind :443 ssl crt /usr/local/etc/haproxy_certs.pem
http-request add-header X-Forwarded-Proto https
acl mail hdr_dom(host) mail.alfaexploit.com
acl prometheus hdr_dom(host) prometheus.alfaexploit.com
acl grafana hdr_dom(host) grafana.alfaexploit.com
acl gdrive hdr_dom(host) gdrive.alfaexploit.com
acl www_alfaexploit hdr_dom(host) www.alfaexploit.com
acl badguys_alfaexploit hdr_dom(host) badguys.alfaexploit.com
acl alfaexploit hdr_dom(host) alfaexploit.com
http-request deny deny_status 400 if !mail !prometheus !grafana !gdrive !www_alfaexploit !badguys_alfaexploit !alfaexploit
# Show banned list to anyone who wants to view it
use_backend badguys if badguys_alfaexploit
# Route Badguys traffic:
acl badguy_ips src -f /usr/local/etc/bagguys.list
use_backend badguys if badguy_ips
# Order matters because acl alfaexploit -> alfaexploit.com is the most generic that covers all of them
use_backend mail if mail
use_backend prometheus if prometheus
use_backend prometheus if grafana
use_backend gdrive if gdrive
use_backend alfaexploit if www_alfaexploit
use_backend alfaexploit if alfaexploit
backend letsencrypt-backend
server letsencrypt 192.168.69.19:88
backend mail
server HellStorm 192.168.69.17:80 check send-proxy-v2
backend prometheus
server RECLog 192.168.69.21:80 check send-proxy-v2
backend gdrive
server Paradox 192.168.69.18:8080 check send-proxy-v2
backend alfaexploit
server MetaCortex 192.168.69.20:80 check send-proxy-v2
backend badguys
http-request set-path / unless { path_beg /images }
server Atlas 192.168.69.19:8888 check send-proxy-v2
Dashboard atacantes
En el servidor donde tendremos la dashboard de atacantes instalaremos Nginx y PHP:
Habilitamos y arrancamos el servicio PHP:
service php-fpm start
Incluimos nuestra configuración desde el fichero global de Nginx:
http {
include badguys.conf;
server {
listen 192.168.69.19:8888 proxy_protocol;
server_name badguys.alfaexploit.com;
set_real_ip_from 192.168.69.19;
real_ip_header proxy_protocol;
root /usr/local/www/nginx;
index index.php;
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(.*)$;
fastcgi_keep_conn on;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
}
}
Habilitamos y arrancamos el servicio Nginx:
service nginx start
Creamos el directorio donde almacenar los logos de los sistemas operativos:
Nos bajamos los logos de los sistemas operativos:
wget https://alfaexploit.com/files/libmodSecurityFreeBSD/images.tar.gz
tar xvzf images.tar.gz<>
El código de la dashboard sería el siguiente:
<?php
$os_array = [
'windows nt 10' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows nt 6.3' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows nt 6.2' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows nt 6.1|windows nt 7.0' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows nt 6.0' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows nt 5.2' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows nt 5.1' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows xp' => 'WindowsXP',
'windows nt 5.0|windows nt5.1|windows 2000' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows me' => 'WindowsME',
'windows nt 4.0|winnt4.0' => 'WindowsNT',
'windows ce' => 'WindowsCE',
'windows 98|win98' => 'Windows98',
'windows 95|win95' => 'Windows95',
'win16' => 'Windows16',
'mac os x 10.1[^0-9]' => 'MacOS',
'macintosh|mac os x' => 'MacOS',
'mac_powerpc' => 'MacOS',
'ubuntu' => 'Linux',
'iphone' => 'iPhone',
'ipod' => 'iPod',
'ipad' => 'iPad',
'android' => 'Android',
'blackberry' => 'BlackBerry',
'webos' => 'WebOS',
'linux' => 'Linux',
'(media center pc).([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2})'=>'WindowsMediaCenter',
'(win)([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9x]{1,2})'=>'Windows',
'(win)([0-9]{2})'=>'Windows',
'(windows)([0-9x]{2})'=>'Windows',
'Win 9x 4.90'=>'WindowsME',
'(windows)([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2})'=>'Windows',
'win32'=>'Windows',
'(java)([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2})'=>'Java',
'(Solaris)([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9x]{1,2}){0,1}'=>'Solaris',
'dos x86'=>'DOS',
'Mac OS X'=>'MacOS',
'Mac_PowerPC'=>'MacOS',
'(mac|Macintosh)'=>'MacOS',
'(sunos)([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2}){0,1}'=>'SunOS',
'(beos)([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2}){0,1}'=>'BeOS',
'(risc os)([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2})'=>'RISCOS',
'unix'=>'Unix',
'os/2'=>'OS2',
'freebsd'=>'FreeBSD',
'openbsd'=>'OpenBSD',
'netbsd'=>'NetBSD',
'irix'=>'IRIX',
'plan9'=>'Plan9',
'aix'=>'AIX',
'GNU Hurd'=>'GNUHurd',
'(fedora)'=>'Linux',
'(kubuntu)'=>'Linux',
'(ubuntu)'=>'Linux',
'(debian)'=>'Linux',
'(CentOS)'=>'Linux',
'(Mandriva).([0-9]{1,3}(\.[0-9]{1,3})?(\.[0-9]{1,3})?)'=>'Linux',
'(SUSE).([0-9]{1,3}(\.[0-9]{1,3})?(\.[0-9]{1,3})?)'=>'Linux',
'(Dropline)'=>'Linux',
'(ASPLinux)'=>'Linux',
'(Red Hat)'=>'Linux',
'(linux)'=>'Linux',
'(amigaos)([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2})'=>'AmigaOS',
'amiga-aweb'=>'AmigaOS',
'amiga'=>'AmigaOS',
'AvantGo'=>'PalmOS',
'[0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,3}'=>'Linux',
'(webtv)/([0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2})'=>'WebTV',
'Dreamcast'=>'DreamcastOS',
'GetRight'=>'Windows',
'go!zilla'=>'Windows',
'gozilla'=>'Windows',
'gulliver'=>'Windows',
'ia archiver'=>'Windows',
'NetPositive'=>'Windows',
'mass downloader'=>'Windows',
'microsoft'=>'Windows',
'offline explorer'=>'Windows',
'teleport'=>'Windows',
'web downloader'=>'Windows',
'webcapture'=>'Windows',
'webcollage'=>'Windows',
'webcopier'=>'Windows',
'webstripper'=>'Windows',
'webzip'=>'Windows',
'wget'=>'Wget',
'Java'=>'Java',
'flashget'=>'FlashGet',
'MS FrontPage'=>'Windows',
'(msproxy)/([0-9]{1,2}.[0-9]{1,2})'=>'Windows',
'(msie)([0-9]{1,2}.[0-9]{1,2})'=>'Windows',
'libwww-perl'=>'Perl',
'UP.Browser'=>'WindowsCE',
'NetAnts'=>'Windows',
];
function user_agent_os($user_agent, $os_array) {
foreach ($os_array as $regex => $value) {
if (preg_match('{\b('.$regex.')\b}i', $user_agent)) {
return $value;
#$key = array_rand($os_array);
#$value = $os_array[$key];
#return $value;
}
}
return 'Unknown';
}
function secs_to_str ($duration) {
$periods = array(
'day' => 86400,
'hour' => 3600,
'minute' => 60,
'second' => 1
);
$parts = array();
foreach ($periods as $name => $dur) {
$div = floor($duration / $dur);
if ($div == 0)
continue;
else
if ($div == 1)
$parts[] = $div . " " . $name;
else
$parts[] = $div . " " . $name . "s";
$duration %= $dur;
}
$last = array_pop($parts);
if (empty($parts))
return $last;
else
return join(', ', $parts) . " and " . $last;
}
if (!empty($_SERVER['HTTP_CLIENT_IP'])) {
$ip_address = $_SERVER['HTTP_CLIENT_IP'];
}
elseif (!empty($_SERVER['HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR'])) {
$ip_address = $_SERVER['HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR'];
}
else {
$ip_address = $_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR'];
}
$redis = new Redis();
$redis->connect('192.168.69.2', 6379);
$redis->auth('XXXXXXXX');
$allKeys = $redis->keys('*');
echo "<!DOCTYPE html>";
echo "<html>";
echo "<head>";
echo "<style>";
echo ".attacker_data {";
echo "position: relative;";
echo "top: -6px;";
echo "padding-left: 8px;";
echo "}";
echo "table, td, th {";
echo "border: 1px solid black;";
echo "margin-bottom: 15px;";
echo "}";
echo "table {";
echo " border-collapse: collapse;";
echo " width: 100%;";
echo "}";
echo "td {";
echo " text-align: center;";
echo "}";
echo "</style>";
echo "</head>";
echo "<body>";
echo "<table>";
echo "<tr>";
echo "<td>Date</td>";
echo "<td>IP</td>";
echo "<td>I'm watching you</td>";
echo "<td>Attack</td>";
echo "<td>Unban remaining time</td>";
echo "</tr>";
foreach ($allKeys as $key) {
$attacker_data = array();
if (str_starts_with($key, 'data')) {
$counter_key = substr($key, 4);
$counter = $redis->get($counter_key);
if ($counter >= 5){
$ttl = $redis->ttl($key);
$ttl_human = secs_to_str($ttl);
$raw_data = $redis->get($key);
$data = explode("++", $raw_data);
$i = 0;
# We are iterating Redis data: 0-> Date, 1 -> attacker_ip, 2 -> useragent_platform, 3 -> useragent, 4 -> message
$get_os_from_useragent = False;
foreach ($data as $field) {
$field = trim($field);
if ($i == 0) {
$attacker_data[] = $field;
} elseif ($i == 1) {
$attacker_ip = $field;
## We have limits requesting /ip-api.com url so we try to cache it
if ($redis->exists('geoipdata'.$attacker_ip)) {
$geoipdata = ($redis->get('geoipdata'.$attacker_ip));
$attacker_data[] = $geoipdata;
} else {
$ips = array();
$ips[] = $field;
$endpoint = 'http://ip-api.com/batch';
$options = [
'http' => [
'method' => 'POST',
'user_agent' => 'AlfaExploit/1.0',
'header' => 'Content-Type: application/json',
'content' => json_encode($ips)
]
];
if (($response = @file_get_contents($endpoint, false, stream_context_create($options))) === false) {
$attacker_data[] = 'UNKNOWN';
# Cache data: 3600s -> 1h
$redis->set('geoipdata'.$attacker_ip, 'UNKNOWN');
$redis->expire('geoipdata'.$attacker_ip, 3600);
} else {
$array = json_decode($response, true);
$status = $array[0]['status'];
if ($status == 'fail' ){
$attacker_data[] = $array[0]['message'];
# Cache data: 3600s -> 1h
$redis->set('geoipdata'.$attacker_ip, $array[0]['message']);
$redis->expire('geoipdata'.$attacker_ip, 3600);
} else {
$country = $array[0]['country'];
$regionName = $array[0]['regionName'];
$lat = $array[0]['lat'];
$lon = $array[0]['lon'];
$isp = $array[0]['isp'];
$attacker_data[] = $country.'/'.$regionName.'('.$lat.' '.$lon.')'. $isp;
# Cache data: 3600s -> 1h
$redis->set('geoipdata'.$attacker_ip, $country.'/'.$regionName.'('.$lat.' '.$lon.')'. $isp);
$redis->expire('geoipdata'.$attacker_ip, 3600);
}
}
}
} elseif ($i == 2) {
# useragent_platform is NULL, continue, we will try to get it from user-agent
if ($field == 'NULL') {
$get_os_from_useragent = True;
} else {
$attacker_data[] = str_replace('"', '', $field);;
}
} elseif ($i == 3 && $get_os_from_useragent) {
# Try to get OS from user-agent
$attacker_data[] = user_agent_os($field, $os_array);
} elseif ($i == 4) {
$attacker_data[] = $field;
}
$i = $i + 1;
}
# Print table data
echo "<tr>";
# DATE:
echo "<td>$attacker_data[0]</td>";
# IP:
if ($ip_address == $attacker_ip) {
echo "<td><span style=\"color:#E20D41;\">$attacker_ip</span></td>";
} else {
echo "<td>$attacker_ip</td>";
}
# ATTACKER DATA
echo "<td><img src=/images/$attacker_data[2].png><span class='attacker_data'>$attacker_data[1]</span></td>";
echo "<td>$attacker_data[3]</td>";
echo "<td>$ttl_human</td>";
echo "</tr>";
}
}
}
echo "</table>";
echo '<a href="https://t.me/AlfaExploia">Telegram channel</a> Email: echo \'a3IwbSAoYXQpIGFsZmFleHBsb2l0IChkb3QpIGNvbQo=\' | base64 -d';
echo '<form action="https://alfaexploit.com">';
echo '<button type="submit">AlfaExploit</button>';
echo '</form>';
echo "</body>";
echo "</html>";
Scripts útiles
Este script nos permitirá ver de forma rápida los atacantes baneados, este script está pensado para ejecutarse en el servidor físico o si se trata de una infraestructura distribuida en el Ha-Proxy, si queremos ejecutarlo en el resto de servidores tan solo debemos eliminar las líneas:
print('')
print('----------------')
print('>> HA-Proxy FILE')
print('----------------')
if os.path.exists(HaProxyBlacklistFile):
HaProxyBlacklist = open(HaProxyBlacklistFile, 'r')
for bannedhost in HaProxyBlacklist.readlines():
bannedhost = bannedhost.replace("\n", "")
print(bannedhost)
print('')
print('----------------')
print('>> HA-Proxy ACL')
print('---------------')
try:
hap = haproxy.HAProxy(socket_dir=HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = True
except:
print('ERRRO: Cant connect to AdminSocket: %s so its impossible to delete attacker IP from blacklist ACL' % HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = False
if canConnectToAdminSocket:
aclCounter = 0
for acl in hap.show_acl():
if acl[0] == '#':
continue
if re.match(BadguysAclPattern, acl):
badguysAclFound = 1
break
aclCounter = aclCounter + 1
if badguysAclFound == 1:
for aclAttackerRaw in hap.show_acl(aclCounter):
aclAttacker = aclAttackerRaw.split(' ')[1]
print(aclAttacker)
#!/usr/local/bin/python
import redis
import os
import subprocess
import re
import time
import datetime
from haproxyadmin import haproxy
HaProxyBlacklistFile = "/usr/local/bastille/jails/Atlas/root/usr/local/etc/bagguys.list"
HaProxyAdminSocketDir = "/usr/local/bastille/jails/Atlas/root/var/run/"
BadguysAclPattern = ".*\(/usr/local/etc/bagguys\.list\) pattern loaded from file '/usr/local/etc/bagguys\.list'.*"
try:
redisconnection = redis.Redis(host="192.168.69.2", port=6379, db=0, password='XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX', charset="utf-8", decode_responses=True)
redisconnection.ping()
except:
print('++ ERROR: Cant connect to redis server')
quit()
print('')
print('---------------')
print('>> REDIS')
print('---------------')
for attacker in redisconnection.scan_iter():
if attacker[0:4] == 'data' or attacker[0:9] == 'geoipdata':
continue
else:
rediscounter = redisconnection.get(attacker)
attackerTTL = redisconnection.ttl(attacker)
remainingTime = str(datetime.timedelta(seconds=attackerTTL))
print("> Attacker: %s Counter: %s" % (attacker, rediscounter))
print("TTL: %s RemainingTime: %s" % (attackerTTL, remainingTime))
if int(rediscounter) >= 5:
print('Banned: YES')
else:
print('Banned: NO')
if redisconnection.get('data' + attacker):
data = redisconnection.get('data' + attacker)
#print("Data: %s" % data)
timestamp = data.split('++')[0]
print("timestamp: %s" % timestamp)
attacker = data.split('++')[1]
#print("attacker: %s" % attacker)
useragent_platform = data.split('++')[2]
print("useragent_platform: %s" % useragent_platform)
useragent = data.split('++')[3]
print("useragent: %s" % useragent)
message = data.split('++')[4]
print("message: %s" % message)
host = data.split('++')[5]
#print("host: %s" % host)
url = data.split('++')[6]
#print("url: %s" % url)
method = data.split('++')[7]
#print("method: %s" % method)
payload = data.split('++')[8]
#print("payload: %s" % payload)
print('')
print('---------------')
print('>> PF')
print('---------------')
bannedhosts = subprocess.run(["pfctl", "-t", "badguys", "-T", "show"], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, text=True)
print("PF Banned hosts: \n%s" % bannedhosts.stdout)
print('')
print('----------------')
print('>> HA-Proxy FILE')
print('----------------')
if os.path.exists(HaProxyBlacklistFile):
HaProxyBlacklist = open(HaProxyBlacklistFile, 'r')
for bannedhost in HaProxyBlacklist.readlines():
bannedhost = bannedhost.replace("\n", "")
print(bannedhost)
print('')
print('----------------')
print('>> HA-Proxy ACL')
print('---------------')
try:
hap = haproxy.HAProxy(socket_dir=HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = True
except:
print('ERRRO: Cant connect to AdminSocket: %s so its impossible to delete attacker IP from blacklist ACL' % HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = False
if canConnectToAdminSocket:
aclCounter = 0
for acl in hap.show_acl():
if acl[0] == '#':
continue
if re.match(BadguysAclPattern, acl):
badguysAclFound = 1
break
aclCounter = aclCounter + 1
if badguysAclFound == 1:
for aclAttackerRaw in hap.show_acl(aclCounter):
aclAttacker = aclAttackerRaw.split(' ')[1]
print(aclAttacker)
Le aseignamos los permisos necesarios:
Al ejecutarlo veremos la siguiente salida:
---------------
>> REDIS
---------------
> Attacker: 192.168.69.202 Counter: 19
TTL: 3522 RemainingTime: 0:58:42
Banned: YES
timestamp: Sat Feb 25 12:56:26 2023
useragent_platform: "Linux"
useragent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/109.0.0.0 Safari/537.36
message: SQL Injection Attack Detected via libinjection
---------------
>> PF
---------------
PF Banned hosts:
192.168.69.202
----------------
>> HA-Proxy FILE
----------------
192.168.69.202
----------------
>> HA-Proxy ACL
---------------
192.168.69.202
Otro script realmente útil es flushear todos los baneos, este script está pensado para ejecutarse en el servidor físico o si se trata de una infraestructura distribuida en el Ha-Proxy, si queremos ejecutarlo en el resto de servidores tan solo debemos eliminar las líneas:
print('')
print('----------------')
print('>> HA-Proxy FILE')
print('----------------')
if os.path.exists(HaProxyBlacklistFile):
try:
open(HaProxyBlacklistFile, 'w').close()
except IOError:
print('Failure')
print('')
print('----------------')
print('>> HA-Proxy ACL')
print('---------------')
try:
hap = haproxy.HAProxy(socket_dir=HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = True
except:
print('ERRRO: Cant connect to AdminSocket: %s so its impossible to delete attacker IP from blacklist ACL' % HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = False
if canConnectToAdminSocket:
aclCounter = 0
for acl in hap.show_acl():
if acl[0] == '#':
continue
if re.match(BadguysAclPattern, acl):
badguysAclFound = 1
break
aclCounter = aclCounter + 1
if badguysAclFound == 1:
for aclAttackerRaw in hap.show_acl(aclCounter):
hap.del_acl(aclCounter, aclAttackerRaw)
#!/usr/local/bin/python
import redis
import os
import subprocess
import re
import datetime
from haproxyadmin import haproxy
HaProxyBlacklistFile = "/usr/local/bastille/jails/Atlas/root/usr/local/etc/bagguys.list"
HaProxyAdminSocketDir = "/usr/local/bastille/jails/Atlas/root/var/run/"
BadguysAclPattern = ".*\(/usr/local/etc/bagguys\.list\) pattern loaded from file '/usr/local/etc/bagguys\.list'.*"
try:
redisconnection = redis.Redis(host="192.168.69.2", port=6379, db=0, password='XXXXXXX', charset="utf-8", decode_responses=True)
redisconnection.ping()
except:
print('++ ERROR: Cant connect to redis server')
quit()
print('')
print('---------------')
print('>> REDIS')
print('---------------')
try:
redisconnection.flushdb()
except:
print('Failure')
print('')
print('---------------')
print('>> PF')
print('---------------')
try:
bannedhosts = subprocess.run(["pfctl", "-t", "badguys", "-T", "flush"], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, text=True)
except:
print('Failure')
print('')
print('----------------')
print('>> HA-Proxy FILE')
print('----------------')
if os.path.exists(HaProxyBlacklistFile):
try:
open(HaProxyBlacklistFile, 'w').close()
except IOError:
print('Failure')
print('')
print('----------------')
print('>> HA-Proxy ACL')
print('---------------')
try:
hap = haproxy.HAProxy(socket_dir=HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = True
except:
print('ERRRO: Cant connect to AdminSocket: %s so its impossible to delete attacker IP from blacklist ACL' % HaProxyAdminSocketDir)
canConnectToAdminSocket = False
if canConnectToAdminSocket:
aclCounter = 0
for acl in hap.show_acl():
if acl[0] == '#':
continue
if re.match(BadguysAclPattern, acl):
badguysAclFound = 1
break
aclCounter = aclCounter + 1
if badguysAclFound == 1:
for aclAttackerRaw in hap.show_acl(aclCounter):
hap.del_acl(aclCounter, aclAttackerRaw)
Le asignamos los permisos necesarios:
Al ejecutarlo veremos la siguiente salida:
---------------
>> REDIS
---------------
---------------
>> PF
---------------
1 addresses deleted.
----------------
>> HA-Proxy FILE
----------------
----------------
>> HA-Proxy ACL
---------------
Resultado final
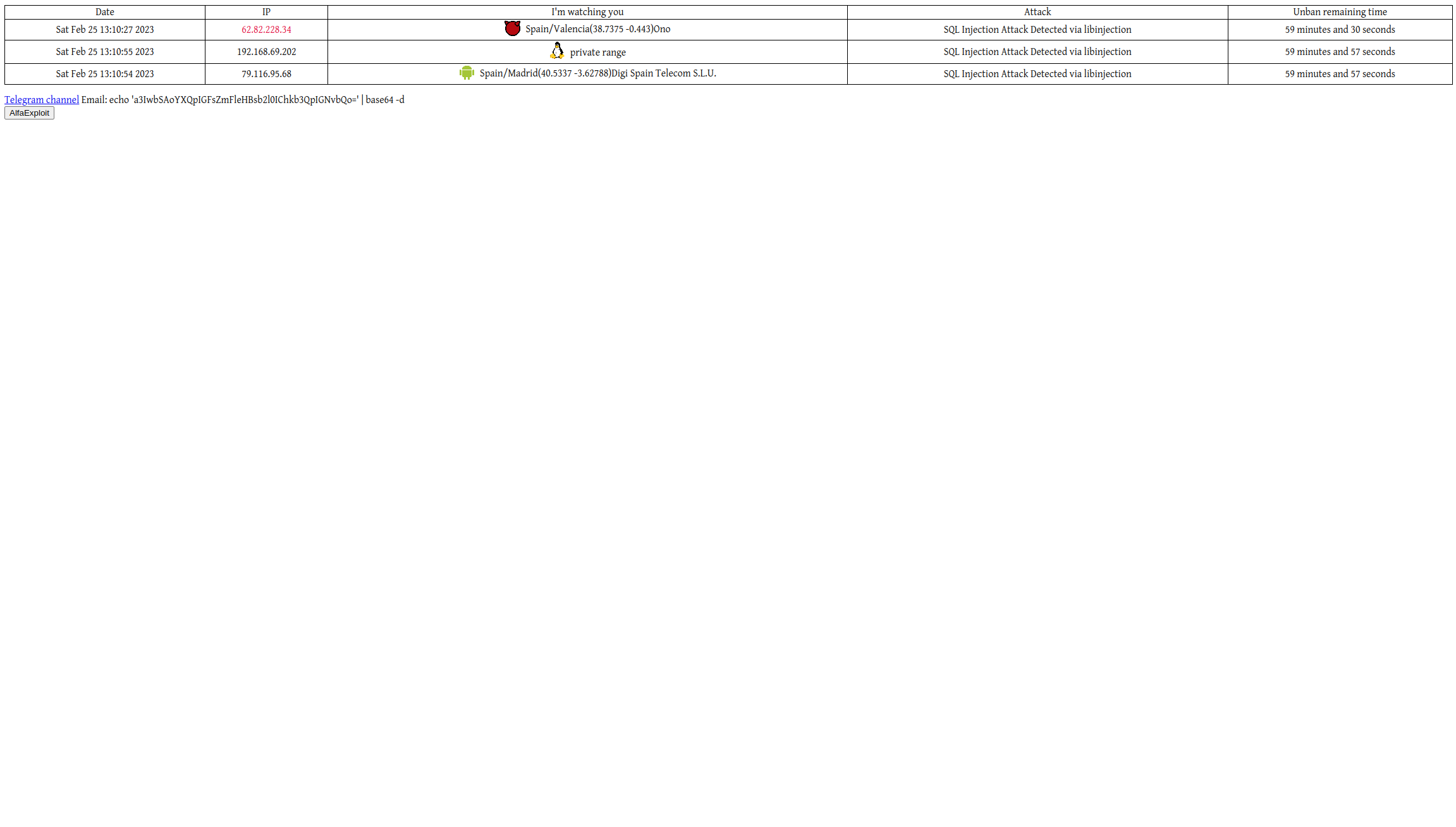
Las notificaciones en Telegram tendrán este aspecto:
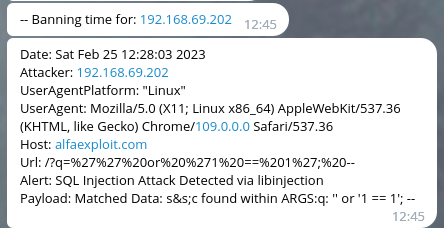
Y el dashboard este: