La salida del comando dmesg en FreeBSD no es demasiado amigable que digamos, además tiene un gran inconveniente y es que no podemos saber la hora en la que se registró cada uno de los eventos, en este tutorial veremos como ingeniárnoslas para habilitar los timestamps y convertirlos a fechas humanas.
En la versión de dmesg de Linux al menos tenemos el parámetro -T con el que ver las fechas directamente pero en FreeBSD sencillamente el parámetro no existe.
dmesg -T
dmesg: illegal option -- T
usage: dmesg [-ac] [-M core [-N system]]
Lo primero que debemos hacer es habilitar el registro de los timestamps a nivel de kernel:
echo 'kern.msgbuf_show_timestamp=1' >> /etc/sysctl.conf
sysctl kern.msgbuf_show_timestamp=1
kern.msgbuf_show_timestamp: 0 -> 1
Y reiniciar:
shutdown -r now
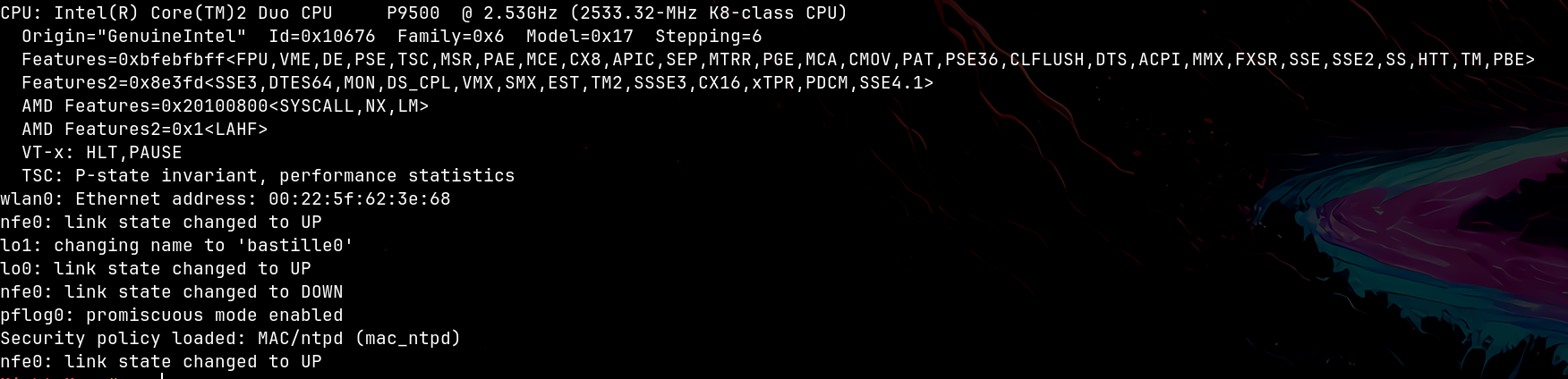
Las marcas de tiempo aparecerán como segundos desde el arranque del sistema:
[30] CPU: Intel(R) Core(TM)2 Duo CPU P9500 @ 2.53GHz (2533.32-MHz K8-class CPU)
[30] Origin="GenuineIntel" Id=0x10676 Family=0x6 Model=0x17 Stepping=6
[30] Features=0xbfebfbff<FPU,VME,DE,PSE,TSC,MSR,PAE,MCE,CX8,APIC,SEP,MTRR,PGE,MCA,CMOV,PAT,PSE36,CLFLUSH,DTS,ACPI,MMX,FXSR,SSE,SSE2,SS,HTT,TM,PBE>
[30] Features2=0x8e3fd<SSE3,DTES64,MON,DS_CPL,VMX,SMX,EST,TM2,SSSE3,CX16,xTPR,PDCM,SSE4.1>
[30] AMD Features=0x20100800<SYSCALL,NX,LM>
[30] AMD Features2=0x1<LAHF>
[30] VT-x: HLT,PAUSE
[30] TSC: P-state invariant, performance statistics
[30] wlan0: Ethernet address: 00:22:5f:62:3e:68
[30] nfe0: link state changed to UP
[30] lo1: changing name to 'bastille0'
[30] lo0: link state changed to UP
[30] nfe0: link state changed to DOWN
[31] pflog0: promiscuous mode enabled
[32] Security policy loaded: MAC/ntpd (mac_ntpd)
[33] nfe0: link state changed to UP
Para convertir los timestamps a fecha humana utilizaremos el siguiente script el cual depende de ccze así que lo instalamos:
pkg install ccze
vi .scripts/dmesg-human.sh
#!/bin/sh
# Get system boot time (Unix timestamp)
boot_time=$(sysctl -n kern.boottime | awk '{print $4}' | tr -d ',')
# Process dmesg output
dmesg | awk -v bt="$boot_time" '
# Preserve boot headers and copyright lines unchanged
/^---<<BOOT>>---/ || /^Copyright/ || /^FreeBSD/ { print; next }
# Convert timestamped lines (e.g., "[8] message")
/^\[[0-9]+\]/ {
gsub(/\[|\]/, "", $1); # Remove brackets from timestamp
ts = $1; # Extract timestamp
$1 = ""; # Remove timestamp from line
# Convert to human-readable time
cmd = "date -j -f %s " (bt + ts) " \"+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S\" 2>/dev/null"
cmd | getline human_time
close(cmd)
printf "[%s]%s\n", human_time, $0
next
}
# Print all other lines as-is
{ print }
' | ccze -A
Asignamos los permisos necesarios:
chmod 700 .scripts/dmesg-human.sh
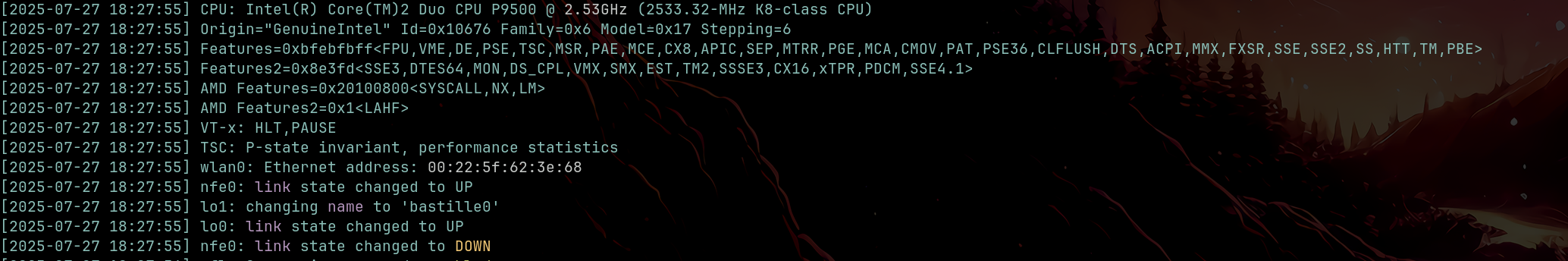
Si ejecutamos el script veremos una salida mucho mas amigable:
.scripts/dmesg-human.sh
| DMESG | DMESG-Script |
|---|---|
|
|