MinIO is a high-performance storage server compatible with Amazon S3. Its main features are hyper-scalable multi-datacenter architecture, high performance for serving large volumes of information, easy non-disruptive upgrade, high availability/failure resistance of disks and/or nodes, support for data encryption and compression.
We compile and install Minio:
We can check the installed version with:
Version: 2019-09-11T19-53-16Z
Release-Tag: DEVELOPMENT.2019-09-11T19-53-16Z
Commit-ID: 3e3fbdf8e6e5e889232eb7afc0b27ac054adfda0
We edit the Minio startup script to assign the ACCESS_KEY and SECRET_KEY:
#!/sbin/openrc-run
# Copyright 2016-2017 Gentoo Foundation
# Distributed under the terms of the GNU General Public License v2
description="Minio Object Storage Server"
pidfile=${pidfile:-"/run/${SVCNAME}.pid"}
export MINIO_ACCESS_KEY=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
export MINIO_SECRET_KEY=YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
command="/usr/bin/minio"
command_args="${command_args:-server /var/lib/minio}"
command_background="true"
start_stop_daemon_args="--stdout /var/log/${SVCNAME}.log \
--stderr /var/log/${SVCNAME}.log"
We start the service and add it to the startup:
rc-update add minio default
By default, Minio starts in mono-server mode exporting the /var/lib/minio directory. We can check that it works correctly by accessing:
http://IP:9000
To use multiple disks (min: 4 disks), we will have to modify the startup script. In this scenario, N/2 disks can be lost without data loss:
#!/sbin/openrc-run
# Copyright 2016-2017 Gentoo Foundation
# Distributed under the terms of the GNU General Public License v2
description="Minio Object Storage Server"
pidfile=${pidfile:-"/run/${SVCNAME}.pid"}
export MINIO_ACCESS_KEY=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
export MINIO_SECRET_KEY=YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
command="/usr/bin/minio"
command_args="${command_args:-server /data1 /data2 /data3 /data4 /data5 /data6 /data7 /data8 /data9 /data10 /data11 /data12}"
command_background="true"
start_stop_daemon_args="--stdout /var/log/${SVCNAME}.log \
--stderr /var/log/${SVCNAME}.log"
We restart the service for the configuration to take effect:
If we check the process, we can see the parameters with which it started:
root 10568 0.0 0.2 2130480 91204 ? Ssl 12:13 0:00 /usr/bin/minio server /data1 /data2 /data3 /data4 /data5 /data6 /data7 /data8 /data9 /data10 /data11 /data12
To perform distributed deployments, we must take into account the following points:
- Minimum number of servers: 2
- Maximum number of servers: 32
- For it to continue working, N/2 disks must remain alive but (N/2)+1 to create new objects.
- Same number of disks on each node.
- All operating systems must be the same OS and have the same bandwidth.
- Clocks must be synchronized with a maximum error of 3s (net-misc/ntpclient).
- Access_keys/secret_keys must be shared between servers.
- The path of the directories used as storage must be the same on all servers.
We assign the same credentials on all servers and in the command arguments we indicate the list of minio servers:
#!/sbin/openrc-run
# Copyright 2016-2017 Gentoo Foundation
# Distributed under the terms of the GNU General Public License v2
description="Minio Object Storage Server"
pidfile=${pidfile:-"/run/${SVCNAME}.pid"}
export MINIO_ACCESS_KEY=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
export MINIO_SECRET_KEY=YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
command="/usr/bin/minio"
command_args="${command_args:-server http://MINIOSERVER1IP/data http://MINIOSERVER2IP/data http://MINIOSERVER3IP/data http://MINIOSERVER4IP/data"
command_background="true"
start_stop_daemon_args="--stdout /var/log/${SVCNAME}.log \
--stderr /var/log/${SVCNAME}.log"
We start the service and add it to the startup on all nodes:
rc-update add minio default
Finally, we install the client on our PC, we must take into account that both the client and the servers must share the same version, in my case the servers are Version: 2019-09-11T19-53-16Z, therefore we download the corresponding version of the client:
chmod +x mc.RELEASE.2019-09-11T20-17-47Z
mv mc.RELEASE.2019-09-11T20-17-47Z /usr/local/bin/mc
We check the version:
Version: 2019-09-11T20:17:47Z
Release-tag: RELEASE.2019-09-11T20-17-47Z
Commit-id: 54ee3a280031adabc49a8309b74e5786cf266706
We configure the credentials of our minio:
export MINIO_ACCESS_KEY=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
export MINIO_SECRET_KEY=YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
We add the servers:
mc config host add kr0mminio2 http://MINIOSERVER2IP:9000 XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
mc config host add kr0mminio3 http://MINIOSERVER3IP:9000 XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
mc config host add kr0mminio4 http://MINIOSERVER4IP:9000 XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
We consult the servers:
kr0mminio
URL : http://MINIOSERVER1IP:9000
AccessKey : XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
SecretKey : YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
API : s3v4
Lookup : auto
kr0mminio2
URL : http://MINIOSERVER2IP:9000
AccessKey : XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
SecretKey : YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
API : s3v4
Lookup : auto
kr0mminio3
URL : http://MINIOSERVER3IP:9000
AccessKey : XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
SecretKey : YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
API : s3v4
Lookup : auto
kr0mminio4
URL : http://MINIOSERVER4IP:9000
AccessKey : XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
SecretKey : YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
API : s3v4
Lookup : auto
From the web interface, I created a bucket called kr0m where I uploaded an image:
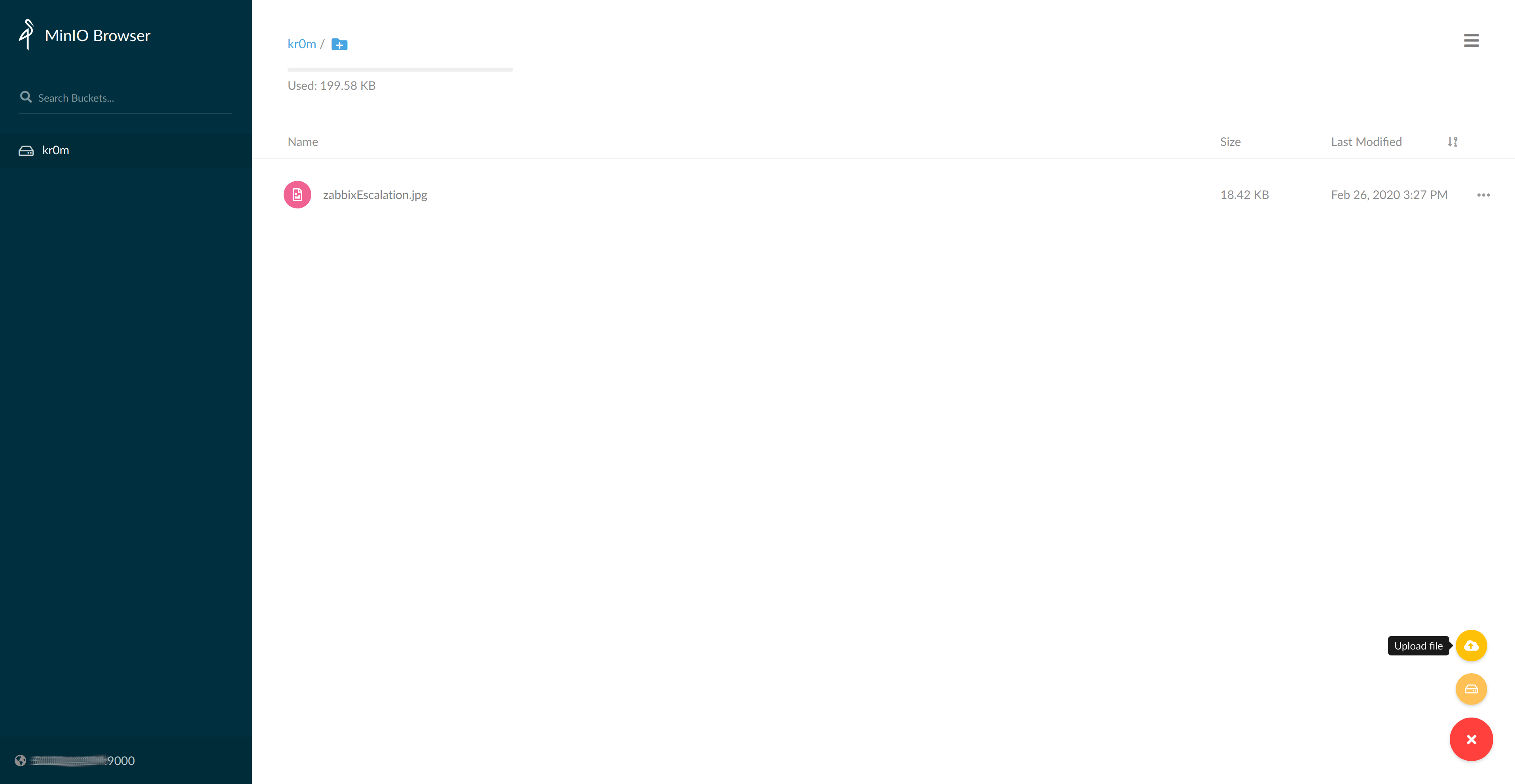
We consult the bucket from CLI:
[2020-02-26 15:27:42 CET] 0B kr0m/
We consult the content of the bucket from CLI:
[2020-02-26 15:27:42 CET] 18KiB zabbixEscalation.jpg
NOTE: If we use mechanical disks, enabling compression usually helps, as it will avoid having to read so much from the disk.
To enable compression, we must dump the current configuration, modify it, and reload it:
vi /tmp/myconfig
"compress": {
"enabled": true,
"extensions": [".txt",".log",".csv", ".json"],
"mime-types": ["text/csv","text/plain","application/json"]
}
We load the modified configuration:
Setting new MinIO configuration file has been successful.
Please restart your server with `mc admin service restart kr0mminio`.
We restart the minio process to apply the configuration.
Restart command successfully sent to `kr0mminio`.
Restarted `kr0mminio` successfully.
NOTE: It should be noted that Minio does not support encryption and compression simultaneously as this would make side-channel attacks such as CRIME and BREACH possible.
An interesting feature of Minio is real-time file synchronization:
touch work/AA
mc mirror work kr0mminio/kr0m
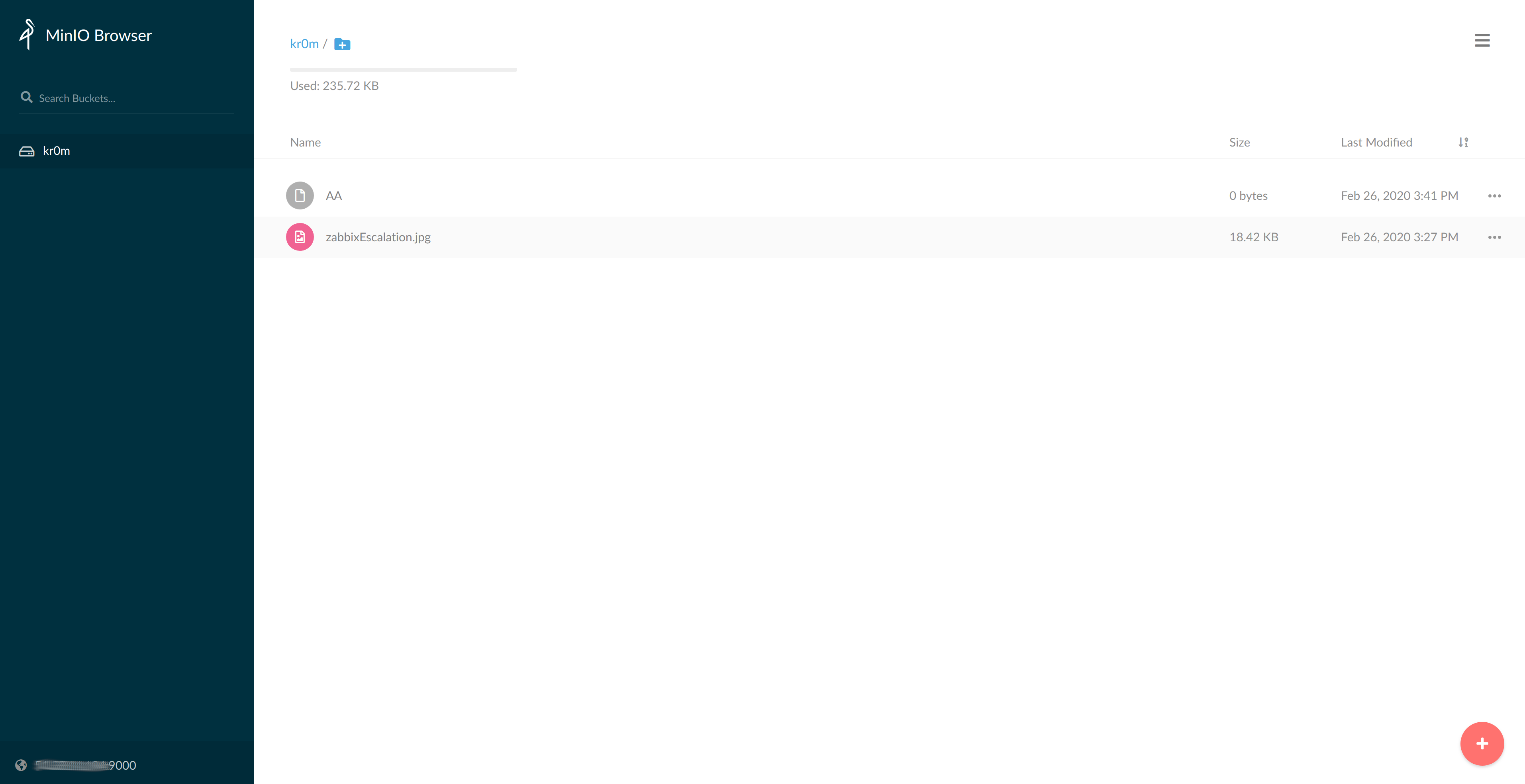
If we enter any other Minio server, we should see the same content:
http://IP:9000
Access permissions are managed through policies:
- none (no anonymous access)
- download (anonymous read-only access)
- upload (anonymous write-only access)
- public (anonymous read/write access)
We can see the policies applied using a get:
Access permission for `kr0mminio/kr0m` is `none`
To assign policies, we will use the set command:
Access permission for `kr0mminio/kr0m` is set to `download`
If we do the get again, we can see that the policy has changed:
Access permission for `kr0mminio/kr0m` is `download`
If we change a disk, we can make the data replicate to the new one with the heal command. First, we must stop the service on the affected node:
We change the disk and start the service again:
From the client, we order it to resynchronize the content:
◓ kr0m/zabbixEscalation.jpg
2/2 objects; 18 KiB in 1s
|--------------------------------------|
| Green | 8 | 100.0% ████████████ │
| Yellow | 0 | 0.0% |
| Red | 0 | 0.0% |
| Grey | 0 | 0.0% |
|--------------------------------------|
To update the Minio versions on the servers, we will use the client:
Server `kr0mminio` already running the most recent version 2019-09-11T19-53-16Z of MinIO
We can see the status of the cluster using the info command:
● MINIOSERVER1IP:9000
Uptime: 1 hour
Version: 2019-09-11T19-53-16Z
Storage: Used 215 KiB, Free 2.4 TiB
Drives: 1/1 OK
CPU min avg max
current 0.11% 0.14% 0.18%
historic 0.05% 0.56% 27.37%
MEM usage
current 70 MiB
historic 70 MiB
● MINIOSERVER2IP:9000
Uptime: 1 hour
Version: 2019-09-11T19-53-16Z
Storage: Used 215 KiB, Free 2.4 TiB
Drives: 1/1 OK
CPU min avg max
current 0.18% 0.23% 0.28%
historic 0.05% 0.52% 35.29%
MEM usage
current 70 MiB
historic 70 MiB
● MINIOSERVER3IP:9000
Uptime: 1 hour
Version: 2019-09-11T19-53-16Z
Storage: Used 215 KiB, Free 2.4 TiB
Drives: 1/1 OK
CPU min avg max
current 0.33% 0.34% 0.36%
historic 0.05% 0.51% 21.96%
MEM usage
current 70 MiB
historic 70 MiB
● MINIOSERVER4IP:9000
Uptime: 1 hour
Version: 2019-09-11T19-53-16Z
Storage: Used 215 KiB, Free 2.4 TiB
Drives: 1/1 OK
CPU min avg max
current 0.14% 0.15% 0.15%
historic 0.05% 0.52% 20.05%
MEM usage
current 70 MiB
historic 70 MiB
Minio allows the export of metrics using Prometheus:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: minio-job
scrape_interval: 1m
scrape_timeout: 10s
metrics_path: /minio/prometheus/metrics
scheme: http
static_configs:
- targets:
- kr0mminio:9000
- kr0mminio2:9000
- kr0mminio3:9000
- kr0mminio4:9000
Some interesting alerts would be when there is a defective disk or when a disk is running out of space:
groups:
- name: Minio
rules:
- alert: DiskOffline
expr: minio_offline_disks != 0
for: 5m
labels:
severity: critical
annotations:
summary: Disk offline
groups:
- name: Minio
rules:
- alert: StorageSpaceExhausted
expr: minio_disk_storage_free_bytes < 10737418240
labels:
severity: info
annotations:
summary: Free space threshold reached
groups:
- name: Minio
rules:
- alert: MinioNodeDown
expr: up{job="minio-job"} == 0
for: 5m
labels:
severity: critical
Through Prometheus, we can visualize the data on the fly, but a more comfortable way is through Grafana. To do this, we will use this dashboard.
Once the dashboard is imported, we will see data like this:
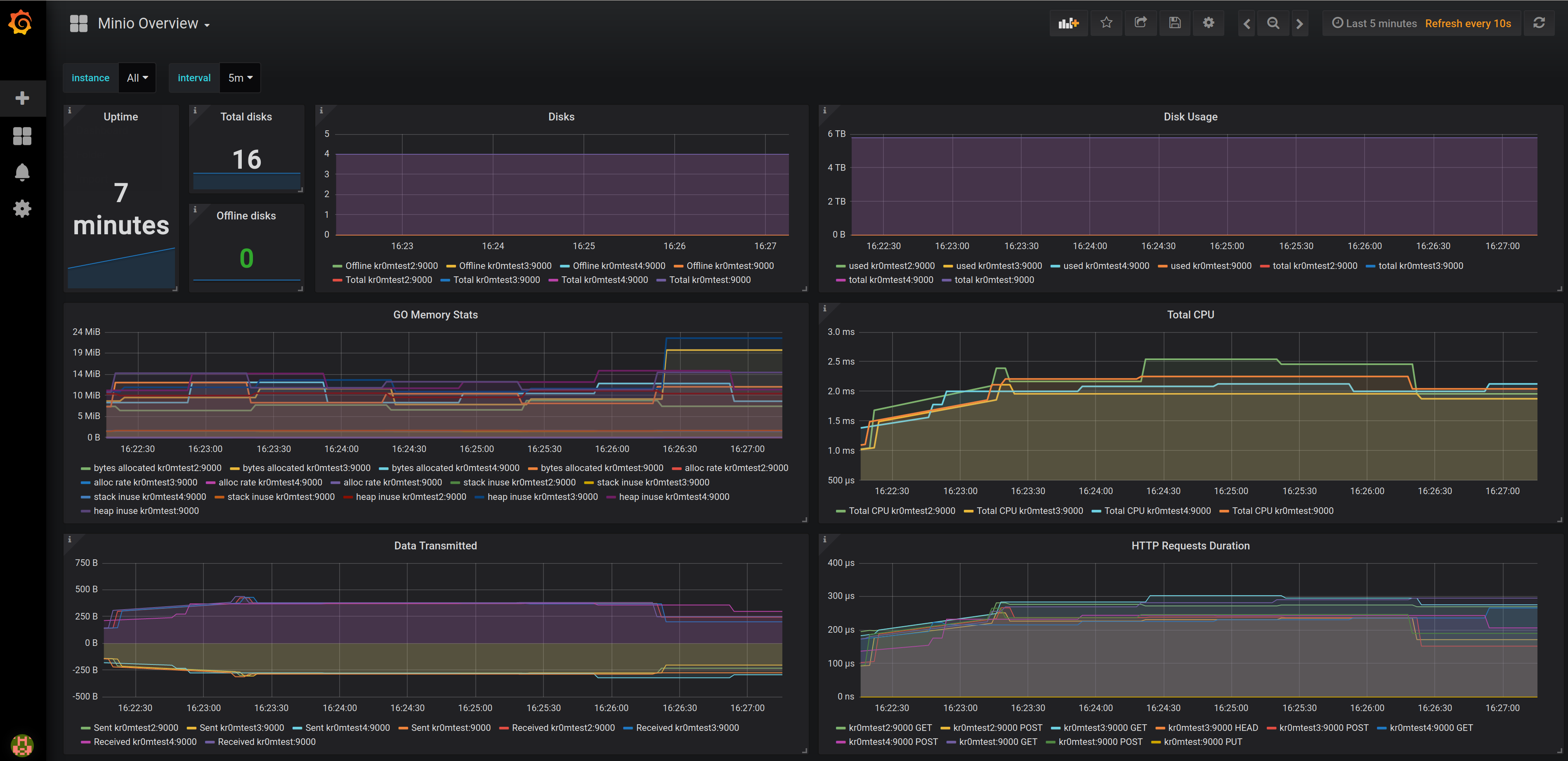
NOTE: There are versions of Minio that do not export the minio_version metric, therefore the instance dropdown will appear empty. To solve this, we must edit the dashboard and in the Variables -> Instance section, change the query to label_values(minio_total_disks,instance)
Encrypting the communications of the Minio nodes will protect us against the theft of sensitive information and allow us to detect alterations of the content.
We generate a certificate for all nodes. If we are going to use IP addresses directly without domains, we will have to generate the certificate in a special way:
cat «-EOF
default_bits = 2048
distinguished_name = dn
x509_extensions = san
req_extensions = san
extensions = san
prompt = no
[ dn ]
countryName = ES
stateOrProvinceName = XXXX
localityName = XXXX
organizationName = Alfaexploit
[ san ]
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[ alt_names ]
IP.1 = MINIOSERVER1IP
IP.2 = MINIOSERVER2IP
IP.3 = MINIOSERVER3IP
IP.4 = MINIOSERVER4IP
EOF
)
Each server will serve the certificate based on public.crt/private.key and will have public.crt as the trusted CA.
scp public.crt kr0mminio:/root/.minio/certs/
scp private.key kr0mminio:/root/.minio/certs/
scp public.crt kr0mminio2:/root/.minio/certs/
scp private.key kr0mminio2:/root/.minio/certs/
scp public.crt kr0mminio3:/root/.minio/certs/
scp private.key kr0mminio3:/root/.minio/certs/
scp public.crt kr0mminio4:/root/.minio/certs/
scp private.key kr0mminio4:/root/.minio/certs/
We modify the script on each of the nodes:
#!/sbin/openrc-run
# Copyright 2016-2017 Gentoo Foundation
# Distributed under the terms of the GNU General Public License v2
description="Minio Object Storage Server"
pidfile=${pidfile:-"/run/${SVCNAME}.pid"}
export MINIO_ACCESS_KEY=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
export MINIO_SECRET_KEY=YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
command="/usr/bin/minio"
#command_args="${command_args:-server /var/lib/minio}"
command_args="${command_args:-server https://MINIOSERVER1IP/data https://MINIOSERVER2IP/data https://MINIOSERVER3IP/data https://MINIOSERVER4IP/data}"
command_background="true"
start_stop_daemon_args="--stdout /var/log/${SVCNAME}.log \
--stderr /var/log/${SVCNAME}.log"
We restart the service:
We also pass the certificates to the mc client so that it can connect without problems:
We update the CA database:
We will have to re-add the nodes in https mode to the client:
mc config host remove kr0mminio2
mc config host remove kr0mminio3
mc config host remove kr0mminio4
mc config host add kr0mminio2 https://MINIOSERVER2IP:9000 XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
mc config host add kr0mminio3 https://MINIOSERVER3IP:9000 XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
mc config host add kr0mminio4 https://MINIOSERVER4IP:9000 XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
We can check the configured servers using the ls command:
NOTE: If we use SSL, we will add the certificate to the Prometheus configuration. We must pass the contents of the public.crt file and take into account that if we have generated the certificates with IP, we will have to enter the IPs and not the domain names in the Prometheus configuration:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: minio-job
scrape_interval: 1m
scrape_timeout: 10s
metrics_path: /minio/prometheus/metrics
scheme: https
tls_config:
ca_file: /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/minio.crt
insecure_skip_verify: false
static_configs:
- targets:
- MINIOSERVER1IP:9000
- MINIOSERVER2IP:9000
- MINIOSERVER3IP:9000
- MINIOSERVER4IP:9000
DEBUG:
The best way to debug problems is to manually start each of the nodes to see the errors by stdout:
We can also check the logs of all servers from the client by connecting to any of the servers: