The best way to provide support to a remote user is through VNC. We could opt for solutions like TeamViewer, but we would be completely trusting that the TeamViewer team is not stealing our data or recording sessions. You know that paranoia is never too much.
This manual is divided into several parts:
VNC Client
Install the VNC server:
From the session of the user who will receive remote support, generate an access password:
Every time the user needs support, they must execute the following command. This way, the VNC server will start so that they can access it remotely:
NOTE: The loop option will cause the VNC server to restart in case of disconnection by the client. If we do not put this option and the client disconnects, the computer will be inaccessible until the user runs the command again.
On the other hand, the technician will have to access through a VNC client:
The connection will be made by indicating the following parameters:
vncviewer IP:5900
VNC Jail
If it is a headless server that we want to access via VNC, we must first start a fake Xorg server that will be displayed by VNC and where we will start our WM.
Install everything you need:
We start dbus:
service dbus start
We add the user to the video group:
We generate an access password from the user:
x11vnc -storepasswd
From the user kr0m, we start the fake graphical server:
We tell the VNC server to display via network the display :0
We start the WM on display :0
We can now access the VNC server:
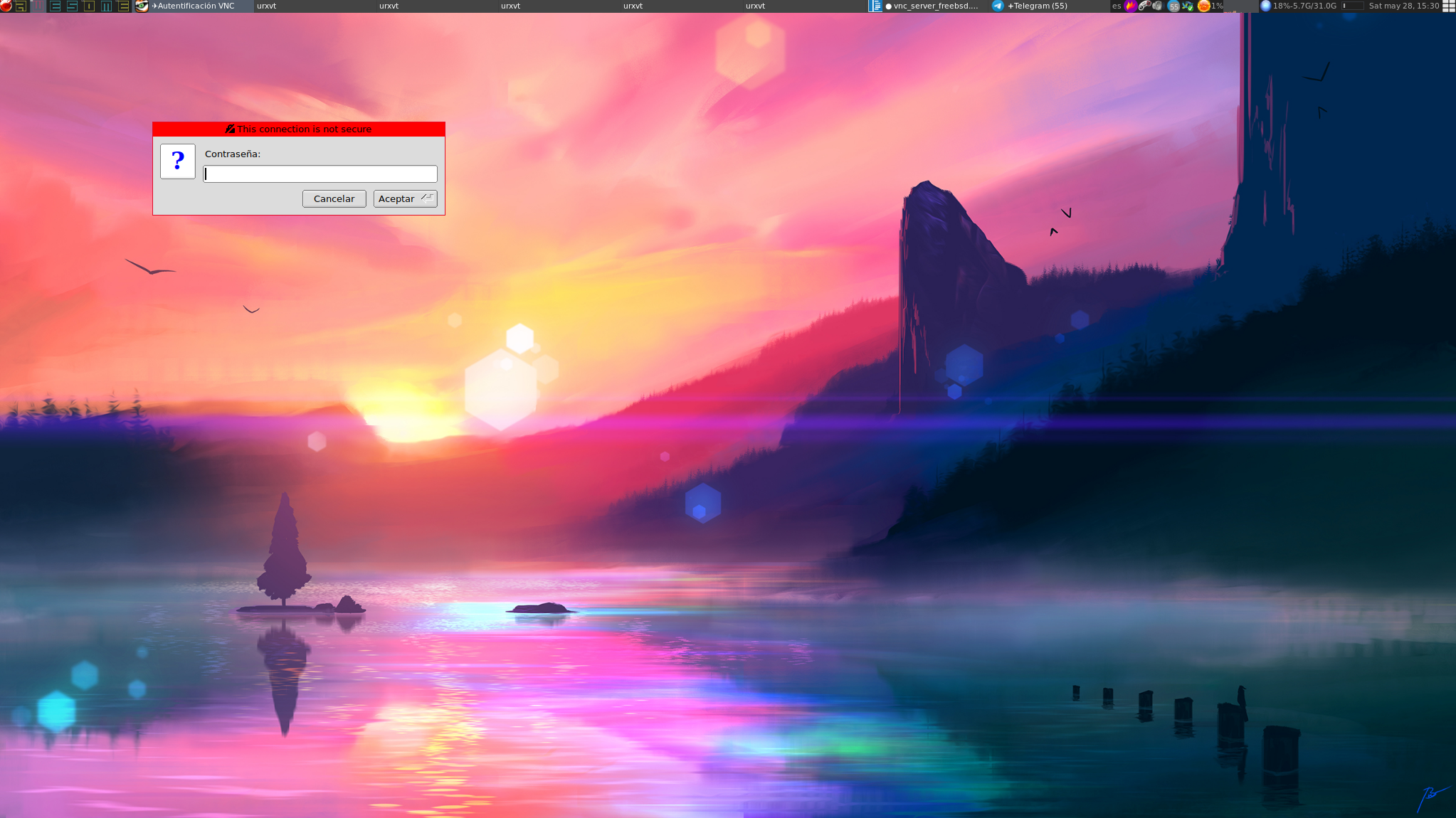
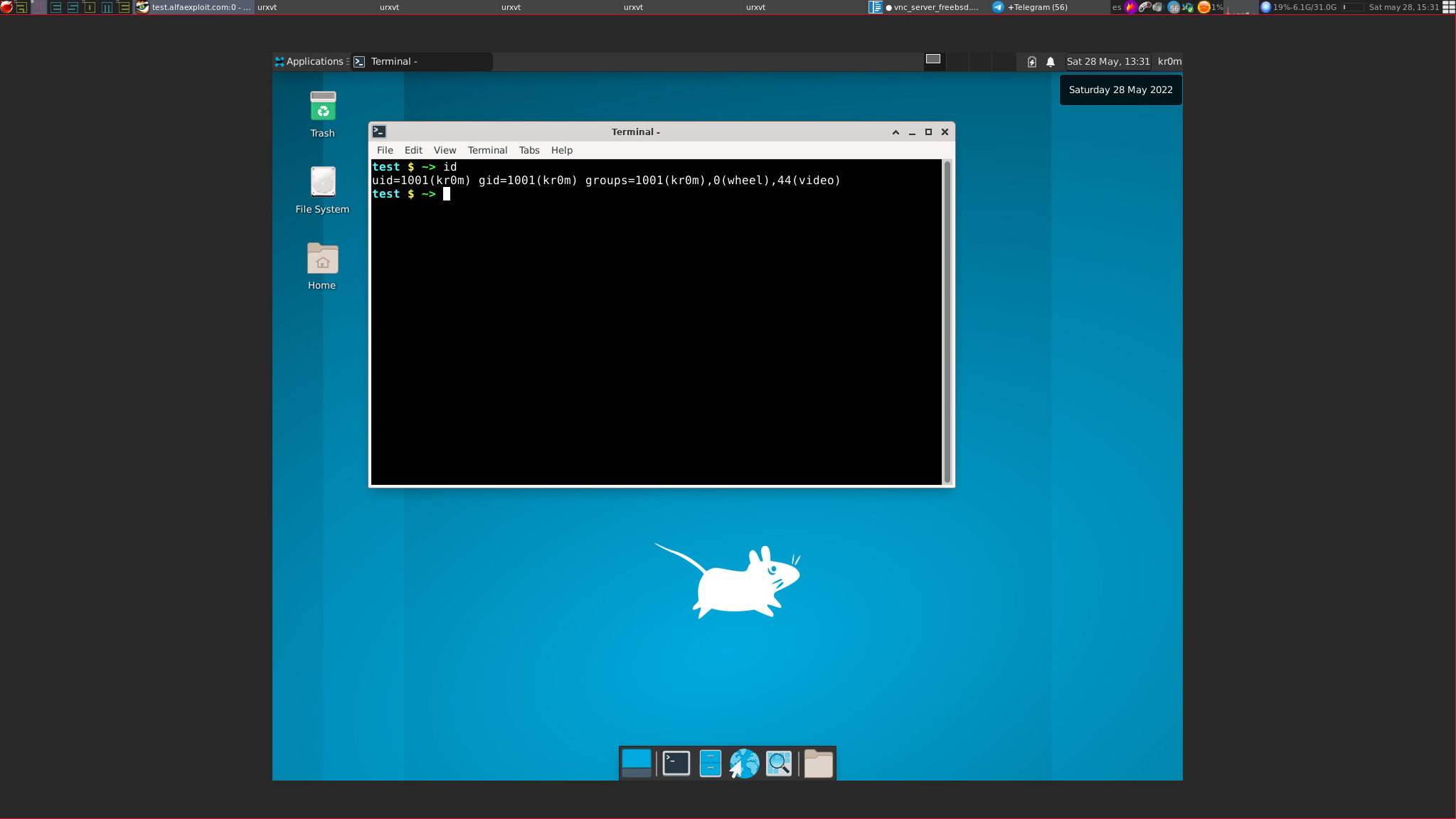
In both cases, whether connecting to the client or to the jail with xvfb, we will be prompted for a password and once authenticated we will access the system:
VNC SSL
The VNC server supports SSL natively, but in many cases, it causes compatibility problems due to incompatible encryption algorithms between the client and the server. To avoid these types of problems, we will use noVNC . This way, we will only worry about the connection from the browser to the noVNC server being encrypted with an SSL certificate and the noVNC server being in clear text until the final server. In addition, access will be more universal since it will be done through an HTML5 browser without the need for a VNC client.
As of 05/28/2022, if we enable SSL, we get this problem:
28/05/2022 21:03:15 SSL: error:1417A0C1:SSL routines:tls_post_process_client_hello:no shared cipher
Due to this bug .
The steps are the same as in the previous scenario, but we will also start the noVNC server.
We start the graphical server:
We start the VNC server:
Starting the WM:
Install git and noVNC:
The noVNC server requires numpy:
Assign the necessary permissions:
Check the allowed parameters by the server:
./utils/novnc_proxy -h
Usage: novnc_proxy [--listen PORT] [--vnc VNC_HOST:PORT] [--cert CERT] [--ssl-only]
Starts the WebSockets proxy and a mini-webserver and
provides a cut-and-paste URL to go to.
--listen PORT Port for proxy/webserver to listen on
Default: 6080
--vnc VNC_HOST:PORT VNC server host:port proxy target
Default: localhost:5900
--cert CERT Path to combined cert/key file, or just
the cert file if used with --key
Default: self.pem
--key KEY Path to key file, when not combined with cert
--web WEB Path to web files (e.g. vnc.html)
Default: ./
--ssl-only Disable non-https connections.
--record FILE Record traffic to FILE.session.js
--syslog SERVER Can be local socket such as /dev/log, or a UDP host:port pair.
--heartbeat SEC send a ping to the client every SEC seconds
--timeout SEC after SEC seconds exit when not connected
--idle-timeout SEC server exits after SEC seconds if there are no
active connections
First, let’s try accessing without SSL. In the following command, we are linking port 5900 with the VNC server started in jail 192.168.69.56:5901:
It will give us a URL like this:
http://test.alfaexploit.com:5900/vnc.html?host=test.alfaexploit.com&port=5900
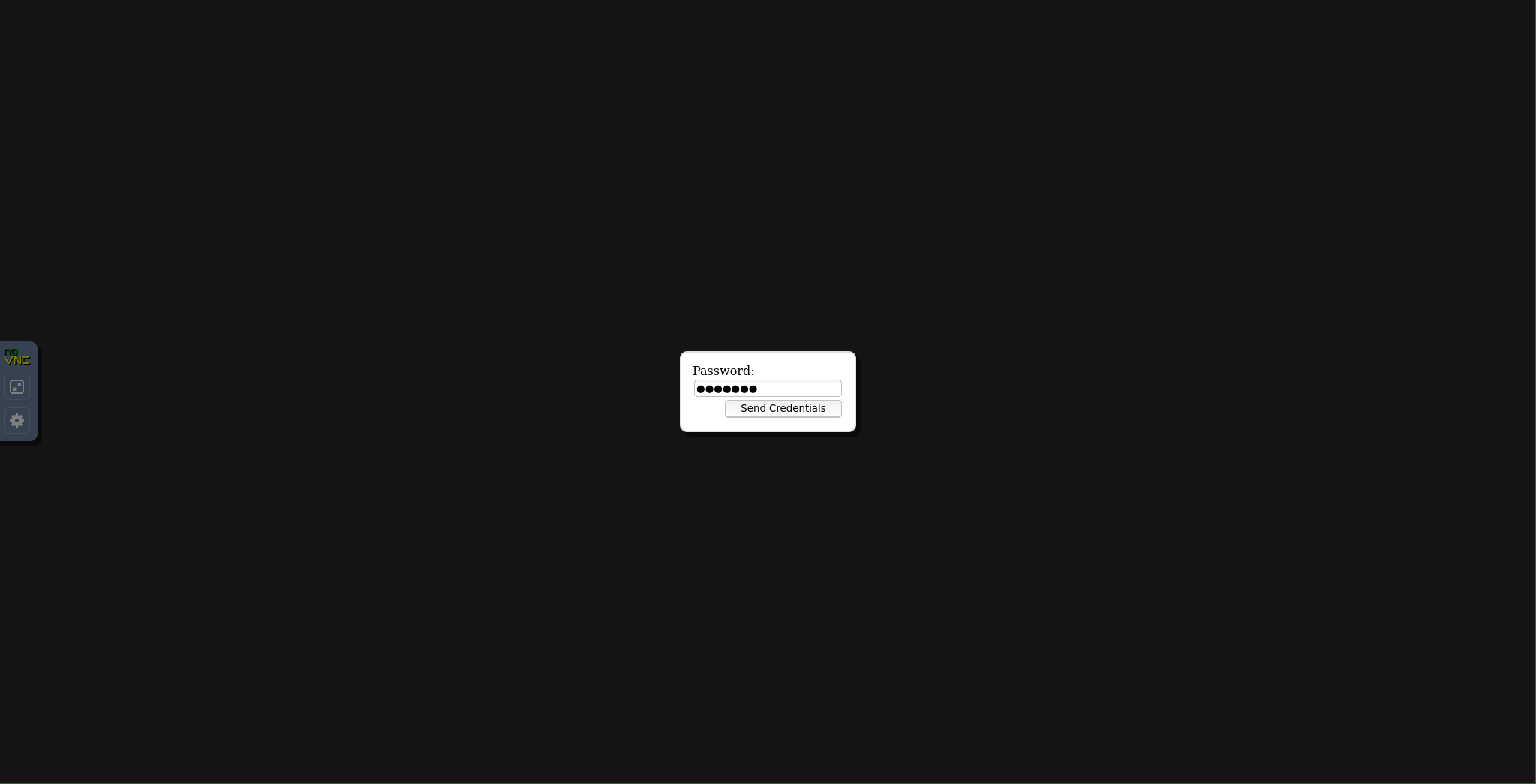
If we access this, we will see an authentication window that corresponds to the password assigned to the VNC server:

Next step is to configure the SSL certificate since there is a login and the password could be intercepted.
We issue the certificate request using
acme.sh
:
curl https://get.acme.sh | sh -s email=kr0m@alfaexploit.com
acme.sh --issue --standalone -d test.alfaexploit.com
[Sat May 28 18:56:17 CEST 2022] Your cert is in: /root/.acme.sh/test.alfaexploit.com/test.alfaexploit.com.cer
[Sat May 28 18:56:17 CEST 2022] Your cert key is in: /root/.acme.sh/test.alfaexploit.com/test.alfaexploit.com.key
[Sat May 28 18:56:17 CEST 2022] The intermediate CA cert is in: /root/.acme.sh/test.alfaexploit.com/ca.cer
[Sat May 28 18:56:17 CEST 2022] And the full chain certs is there: /root/.acme.sh/test.alfaexploit.com/fullchain.cer
Start the noVNC server with SSL parameters:
./utils/novnc_proxy --vnc 192.168.69.56:5901 --cert /root/.acme.sh/test.alfaexploit.com/fullchain.cer --key /root/.acme.sh/test.alfaexploit.com/test.alfaexploit.com.key --listen 5900 --ssl-only
It will give us a URL like this:
https://test.alfaexploit.com:5900/vnc.html?host=test.alfaexploit.com&port=5900
The content of the web will be the same but this time the traffic will be encrypted:
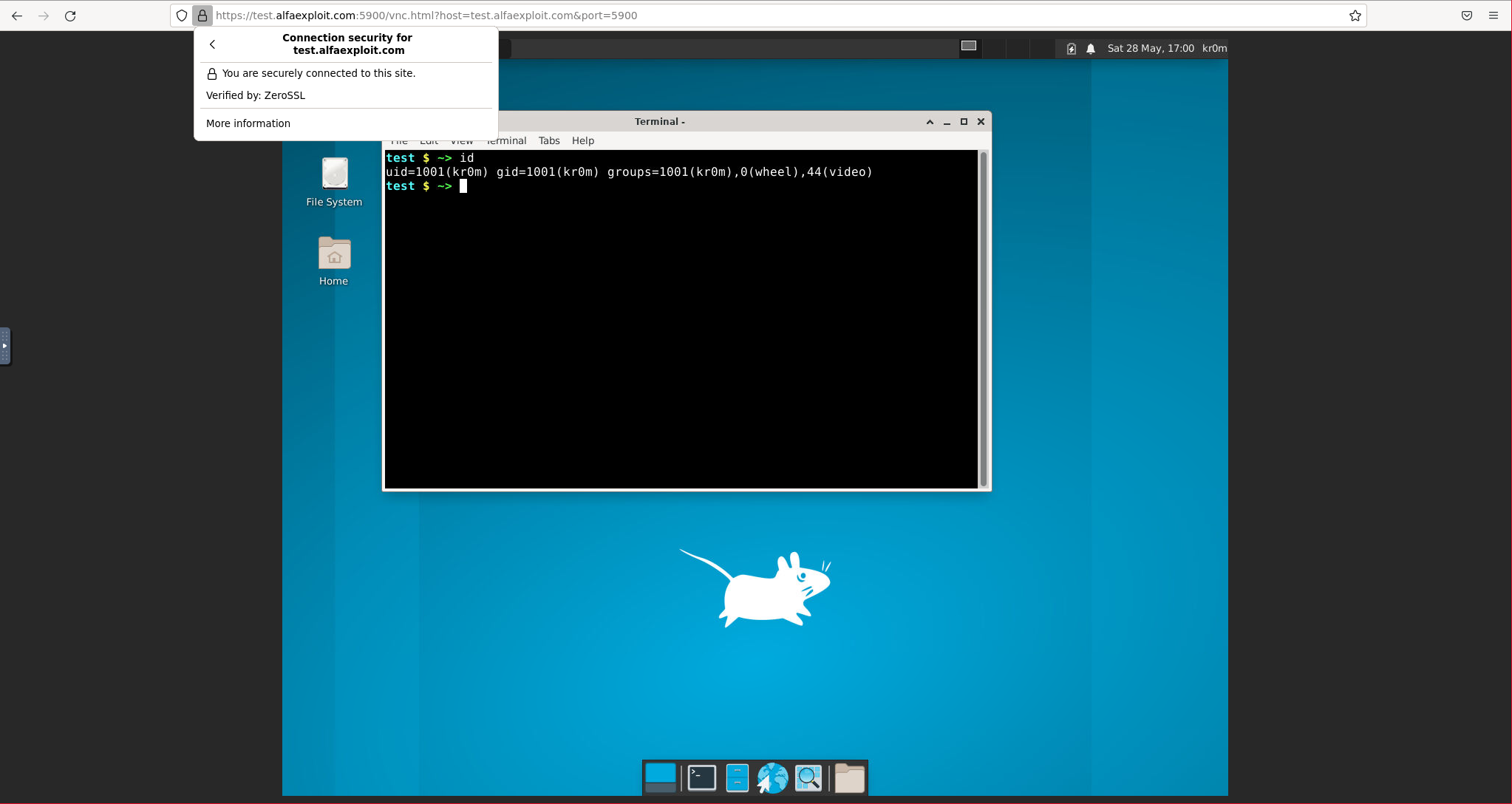
VNC SSL Daemon
To make all of this start automatically, we will create an RC script:
#! /bin/sh
#
# $FreeBSD$
#
# PROVIDE: vnc
# REQUIRE: DAEMON
# KEYWORD: shutdown
. /etc/rc.subr
name="vnc"
extra_commands="status"
username="kr0m"
start_cmd="${name}_start"
stop_cmd="${name}_stop"
status_cmd="${name}_status"
vnc_start(){
PID=$(ps -U ${username}|grep Xvfb|grep -v grep|awk '{print$1}')
if [ -z $PID ]; then
echo "Starting service: Xvfb"
/bin/rm /tmp/.X*-lock 2>/dev/null
/usr/bin/su -l ${username} -c '/usr/bin/nohup /usr/local/bin/Xvfb :0 > /dev/null 2>&1 &' 1>/dev/null
else
echo "Service: Xvfb already started"
fi
PID=$(ps -U ${username}|grep x11vnc|grep -v grep|awk '{print$1}')
if [ -z $PID ]; then
echo "Starting service: X11vnc"
/usr/bin/su -l ${username} -c '/usr/bin/nohup /usr/local/bin/x11vnc -usepw -rfbport 5901 -display :0 -noshm -forever -shared > /dev/null 2>&1 &' 1>/dev/null
else
echo "Service: x11vnc already started"
fi
PID=$(ps -U ${username}|grep xfce4-session|grep -v grep|awk '{print$1}'|sort|head -n 1)
if [ -z $PID ]; then
echo "Starting service: XFCE"
/usr/bin/su -l ${username} -c 'export DISPLAY=:0 && /usr/bin/nohup /usr/local/bin/startxfce4 > /dev/null 2>&1 &' 1>/dev/null
else
echo "Service: x11vnc already started"
fi
# WEBSOCKIFY launches more than one thread in that way we have to check the number of running threads
WEBSOCKIFY_N=$(ps -U root|grep websockify|grep -v grep|wc -l|awk '{print$1}')
if [ $WEBSOCKIFY_N -eq 0 ]; then
echo "Starting service: Websockify"
PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/root/bin
/usr/bin/nohup /usr/local/bin/bash /usr/local/libexec/novnc/utils/novnc_proxy --vnc 192.168.69.56:5901 --cert /root/.acme.sh/test.alfaexploit.com/fullchain.cer --key /root/.acme.sh/test.alfaexploit.com/test.alfaexploit.com.key --listen 5900 --ssl-only > /dev/null 2>&1 & 1>/dev/null
else
echo "Service: Websockify already started"
fi
/bin/rm /home/${username}/nohup.out 2>/dev/null
/bin/rm /root/nohup.out 2>/dev/null
}
vnc_stop(){
PID=$(ps -U ${username}|grep Xvfb|grep -v grep|awk '{print$1}')
if [ -z $PID ]; then
echo "It appears Xvfb is not running."
else
echo "Stopping service: Xvfb/X11vnc/XFCE"
kill -s INT $PID
sleep 3
fi
# WEBSOCKIFY launches more than one thread in that way we have to check the number of running threads
WEBSOCKIFY_N=$(ps -U root|grep websockify|grep -v grep|wc -l|awk '{print$1}')
if [ $WEBSOCKIFY_N -eq 0 ]; then
echo "It appears Websockify is not running."
else
echo "Stopping service: Websockify"
for PID in $(ps -U root|grep websockify|grep -v grep|awk '{print$1}'); do
kill -s INT $PID
done
sleep 3
fi
}
vnc_status(){
PID=$(ps -U ${username}|grep Xvfb|grep -v grep|awk '{print$1}')
if [ -z $PID ]; then
echo "Xvfb is not running."
else
echo "Xvfb running with PID: $PID"
fi
PID=$(ps -U ${username}|grep x11vnc|grep -v grep|awk '{print$1}')
if [ -z $PID ]; then
echo "x11vnc is not running."
else
echo "X11vnc running with PID: $PID"
fi
PID=$(ps -U ${username}|grep xfce4-session|grep -v grep|awk '{print$1}'|sort|head -n 1)
if [ -z $PID ]; then
echo "XFCE is not running."
else
echo "XFCE running with PID: $PID"
fi
# WEBSOCKIFY launches more than one thread in that way we have to check the number of running threads
WEBSOCKIFY_N=$(ps -U root|grep websockify|grep -v grep|wc -l|awk '{print$1}')
if [ $WEBSOCKIFY_N -eq 0 ]; then
echo "Websockify is not running."
else
echo "Websockify running with PIDS:"
for PID in $(ps -U root|grep websockify|grep -v grep|awk '{print$1}'); do
echo "PID: $PID"
done
sleep 3
fi
}
load_rc_config ${name}
run_rc_command "$1"
Assign the necessary permissions:
chown root:wheel /usr/local/etc/rc.d/vnc
Enable and start the service:
service vnc start
With this script, all processes will start automatically on each reboot.