If you are as paranoid as I am, you may always have the idea in your head that one of your servers may be compromised without even knowing it. In this article, I will explain how to program a simple log parser using Python, so that when an SSH access occurs, we will be notified via Telegram.
To improve the security of the SSH service, we will first deny root access to the server and disable password access:
PermitRootLogin no
PubkeyAuthentication yes
PasswordAuthentication no
ChallengeResponseAuthentication no
UsePAM yes
Restart the service:
Our parsing script will need some dependencies, so we install Python and Pip:
Install the dependencies using Pip:
The parser will have the following code:
#!/usr/local/bin/python
import time
import os
import re
import requests
import socket
print('')
print('---------------------------------')
print('| Auth Log Parser v0.1b by kr0m |')
print('---------------------------------')
def sendMessage(msg):
apiKey = "API_KEY"
userId = "USER_ID"
data = {"chat_id":userId,"text":msg}
url = "https://api.telegram.org/bot{}/sendMessage".format(apiKey)
r = requests.post(url,json=data)
logfile = open("/var/log/auth.log","r")
logfile.seek(0, os.SEEK_END)
while True:
logline = logfile.readline()
if not logline:
time.sleep(0.1)
continue
else:
#print('- LogLine: %s' % logline)
m = re.search(".*Accepted (.*) for (.*) from (.*) port.*", logline)
if m:
print('>> SSH LogIN -> User: %s - IP: %s - AuthType: %s' % (m.group(2), m.group(3), m.group(1)))
hostname = socket.gethostname()
message = 'SSH LogIN: '+hostname+'\n User: '+m.group(2)+'\n IP: '+m.group(3)+'\n AuthType: '+m.group(1)
sendMessage(message)
continue
m = re.search(".*Disconnected from user (.*) (.*) port.*", logline)
if m:
print('>> SSH LogOut -> User: %s - IP: %s' % (m.group(1), m.group(2)))
hostname = socket.gethostname()
message = 'SSH LogOut: '+hostname+'\n User: '+m.group(1)+'\n IP: '+m.group(2)
sendMessage(message)
continue
Assign the necessary permissions:
Daemonize the script using an RC script:
#! /bin/sh
#
# $FreeBSD$
#
# PROVIDE: sshAccess
# REQUIRE: DAEMON
# KEYWORD: shutdown
. /etc/rc.subr
name="sshAccess"
rcvar="${name}_enable"
extra_commands="status"
start_cmd="${name}_start"
stop_cmd="${name}_stop"
status_cmd="${name}_status"
sshAccess_start(){
echo "Starting service: ${name}"
/usr/sbin/daemon -S -p /var/run/${name}.pid -T sshAccess -u root /root/.scripts/sshAccess.py
}
sshAccess_stop(){
if [ -f /var/run/${name}.pid ]; then
echo "Stopping service: ${name}"
kill -s INT $(cat /var/run/${name}.pid)
sleep 3
else
echo "It appears ${name} is not running."
fi
}
sshAccess_status(){
if [ -f /var/run/${name}.pid ]; then
echo "${name} running with PID: $(cat /var/run/${name}.pid)"
else
echo "It appears ${name} is not running."
fi
}
load_rc_config ${name}
run_rc_command "$1"
Assign the necessary permissions and owner/group to the RC script:
chown root:wheel /usr/local/etc/rc.d/sshAccess
Enable the service and start it:
service sshAccess start
When someone accesses our server, we will receive a notification like this:
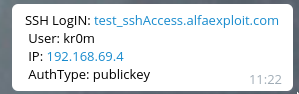
Also, when they log out:
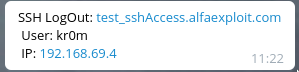
If it wasn’t us, something smells fishy. Most likely, our server has been compromised.